Home » Posts tagged 'W. Tatarkiewicz'
Tag Archives: W. Tatarkiewicz
Philosophy in Zielona Góra. An Anniversary
This year, Institute of Philosophy, University of Zielona Góra (UZ), where Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group is affiliated, celebrates its 30th anniversary. Among the variety of events, there was a conference on 23rd-24th October, devoted to the problem of co-operation in its various relations to theory, history and philosophical practice. AΦR’s history at UZ is obviously much shorter, but two of its representatives actively participated in the conference.

Mariam Sargsyan was the first of them. In her presentation she discussed the results of her doctoral studies at UZ and her dissertation, successfully defended earlier this year. She focused on analyses of Henryk Jakubanis’ (1879-1949) historical-philosophical legacy, which consists of three main parts: 1) his work on Empedocles and its methodology; 2) Plato in his (partly unpublished) writings; 3) his views on ancient and modern ways of doing philosophy. Moreover, Sargsyan presented the conclusions of her research on intellectual genealogy of Jakubanis’ thought.

What was even more significant was the fact that Ukrainian participants (see the photo above) of the conference, who work at the National University of Kyiv, attended Sargsyan’s presentation on Jakubanis, who had studied and worked in Kyiv a century ago. They were very interested in her results and provided valuable feedback that could be helpful in improving the text of her doctoral thesis before it is published. The discussion between them demonstrated how important it is to confront different points of view on one subject which is researched by scholars from different countries, applying various methods and interested in different aspects of the history of philosophy.
The second conference participant from AΦR was Adrian Habura who delivered a paper on Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980) and his reflection on social aspects of human happiness. Habura discussed Tatarkiewicz’s definition of happiness and his understanding of human life, then he examined the role of the others in individual happiness and the links between human individual and society in their relations to happiness. In his paper Habura developed a general view on the role of society in Tatarkiewicz’s philosophical and ethical considerations contained in his book Analysis of Happiness.
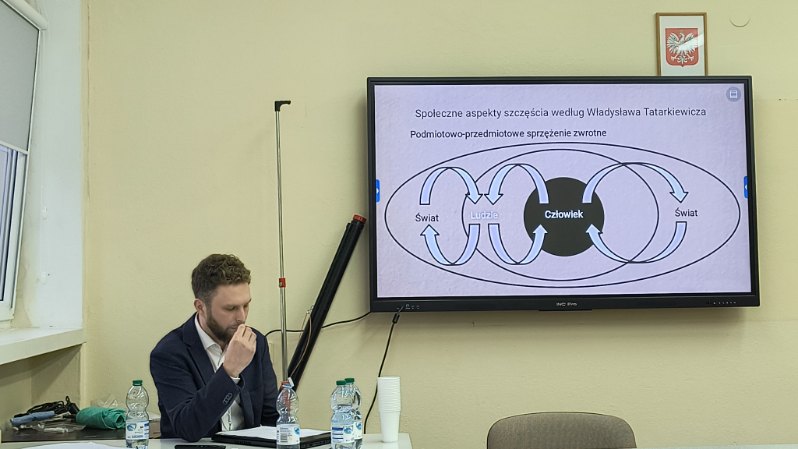
Although Habura’s paper was not directly devoted to the reception of ancient philosophy in Tatarkiewicz’s writings, the following discussion allowed him to address this issue. He highlighted some similarities and differences between Aristotle’s and Tatarkiewicz’s understandings of happiness and convincingly demonstrated how Aristotle could have inspired ethical investigations of this Polish philosopher, whose doctoral thesis on Aristotle was composed under supervision of the Marburg neo-Kantians.
Ancient Φilosophy Reception at the 12th Seminar of Historians of Polish Philosophy

Seminar of Historians of Polish Philosophy (SHPPh) is a cyclical academic event held at various universities in Poland since its first edition in Warsaw in 2006. In 2025 (May 19th-20th), it was for the first time at the University of Zielona Góra (UZ) where Polish researchers of their native philosophical traditions gathered. Central topic of this edition of SHPPh was the problem of classical thinkers and epigons in the development of Polish thought. Detailed programme of the whole event can be downloaded here.
The seminar was also an opportunity to celebrate the second edition of the book Classics of Polish Philosophy by Ryszard Palacz, an essential figure for historians of philosophy at UZ, and a researcher of reception of Greek philosophy in medieaval thought, about whose passing we have informed in the autumn of 2024. Full program of the event can be downloaded here and a brief report (in Polish) on the UZ’s website can be found here (with a photo gallery). The seminar was accompanied by an exhibition devoted to Professor Palacz and many speakers referred to his work and his understanding of classical Polish philosophers.


Two AΦR group members delivered their papers during the SHPPh. Tomasz Mróz talked about Bohdan Kieszkowski (1903-1997) and about Polish and international disputes on his works on Florentine Platonism.
In the thirties in Poland Kieszkowski was engaged in a dispute with Marian Heitzman (1899-1964), who accused him of underestimating the influences of medieval neoplatonism on Ficino. Heitzman and Kieszkowski, two scholars of one generation, two researchers of Renaissance Platonism, represented two different academic centres, conservative Cracow and more progressive Warsaw, and their polemical texts were published separately in philosophical journals in Cracow (Heitzman) and Warsaw (Kieszkowski). Kieszkowski, naturally, considered Heitzman’s position to be an overestimation of medieval influences on Renaissance’s thought and labelled it as ‘medievalism’. On international niveau a polemic against Kieszkowski’s work came from a Portuguese scholar, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010), who praised Kieszkowski’s scholarship, yet spared no words of criticism against Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico della Mirandola’s Conclusiones (Geneve 1973).
Adrian Habura’s talk smoothly concluded the whole conference focusing, on the one hand, on a paper titled Four Understandings of Classicism by Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980), and on the other hand, on Palacz’s (1935-2024) arguments for including Tatarkiewicz among the classics of Polish philosophy.

Habura analysed Tatarkiewicz’s notion of classicism and supplemented Palacz’s arguments for including Tatarkiewicz among the classics, demonstrating that not only his History of Philosophy, History of Aesthetics, and History of Six Ideas, that is, basically historical studies, but also his Analysis of Happiness, the original philosophical work by Tatarkiewicz, bears the mark of classic. Ethical considerations in the Analysis of Happiness, noticeably influenced by Aristotle, not to mention Tatarkiewicz’s doctoral degree from Marburg on a thesis devoted to Aristotle, allowed Habura to highlight an additional aspect of Tatarkiewicz as a classic, for he was not only a classic among Polish philosophers, but also a classic in another understanding: as a follower or – to use the term proposed by Juliusz Domański – a user of Aristotelian philosophy. And it was Aristotle whom Tatarkiewicz himself regarded as the most classical among all the classical philosophers of ancient Greece.
A Guest from Vilnius University
In the last week of November Institute of Philosophy hosted an Erasmus+ visitor from Vilnius University, prof. Jonas Čiurlionis, a long-time collaborator of Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group. It was his second visit in Zielona Góra. One of the tasks of our guest was to consult conclusions of the dissertation by Adrian Habura, the topic of which is a multifaceted reception of Aristotle in Władysław Tatarkiewicz’s oeuvre. It is sufficient to add that prof. J. Čiurlionis is Habura’s auxiliary supervisor.
The most important, however, were Čiurlionis’ lectures and talks for students of philosophy and related fields of study. During the first of them he discussed Aristotle’s Physics. He focused not only on the most significant problems of this work, as, for example, the theory of four elements, but also presented the broader context of Stagirite’s reflection, his fundamental premises and his general view of the world. At the end of the lecture, prof. Čiurlionis referred to Carlo Rovelli, a theoretical physicist, who considers Aristotelian physics to be still topical and not outdated.
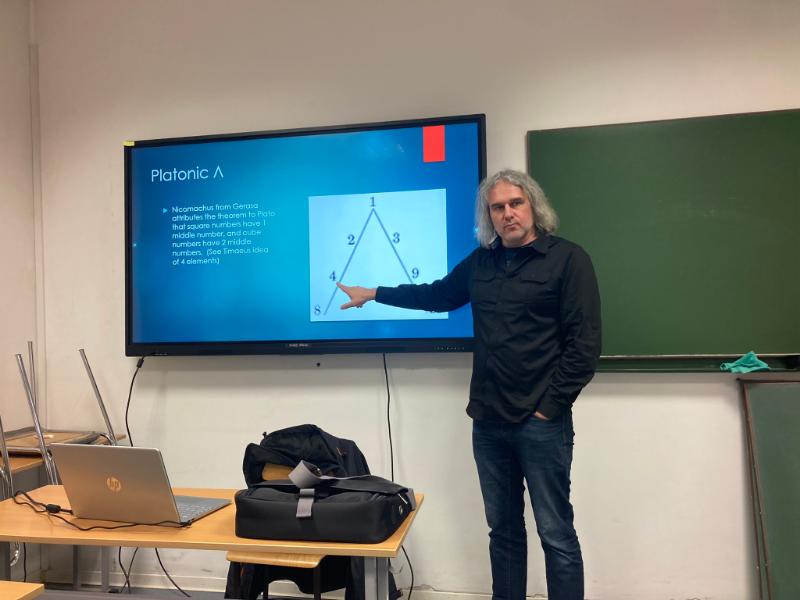

The second lecture on ancient philosophy was devoted to the subject of harmony, broadly considered. Starting with Pythagorean and Platonic concepts, prof. Čiurlionis moved on to other authors dealing with this issue and demonstrated how harmony manifested itself in various aspects of ancient Greek philosophy and, more broadly, in Greek culture, and in subsequent centuries, in music and astrology.
AΦR at the 3rd Congress on Polish Philosophy
The 3rd Congress on Polish Philosophy took place in October (18th-20th) in the Rydzyna Palace. It gathered scholars interested in researching the tradition of Polish philosophy and developing it. Two members of the Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group took part in this philosophical event: Adrian Habura – online, and Tomasz Mróz – onsite. The first of them spoke about the concept of love in the works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980), while the latter – on the history of studies on the reception of ancient philosophy in Poland.
Mróz’s paper was directly concerned with problems related to the reception of ancient philosophy and started with quotes of diverse opinions of two eminent Polish researchers in the history of Greek philosophy, that is, Stefan Pawlicki (1839-1916) and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954). Lutosławski, when composing his works on Plato, searched for Polish authors and their studies to provide references to them, while Pawlicki paid no interest to the works of his compatriots on Greek philosophy.
In more recent decades it was Izydora Dąmbska (1904-1983), a philosopher and historian of philosophy, who published a study on the reception of Plato in Poland (1972), but nowadays many books and papers on this topic were published by the members of the AΦR research group. Concluding his talk Mróz briefly presented research projects of the members of the AΦR and the books they had published, to start with the latest one:

Henryk Jakubanis, Empedokles – filozof, lekarz i mag: Przyczynek do jego zrozumienia i oceny (Empedocles: a Philosopher, a Doctor and a Magus. Materials for Understanding and Assessing Him), transl. from Russian and ed. Mariam Sargsyan, A. Habura, Wydawnictwo Marek Derewiecki, Kęty 2024, 104 pp. (Studies and Texts in the History of Reception of Ancient Philosophy, vol. 3).
T. Mróz, Stanisław Lisiecki (1872-1960) i jego Platon (Stanisław Lisiecki (1872-1960) and His Plato), Wydawnictwo Marek Derewiecki, Kęty 2022, 150 pp. (Studies and Texts in the History of Reception of Ancient Philosophy, vol. 2).


T. Mróz, Plato in Poland 1800-1950: Types of Reception – Authors – Problems, Academia Verlag / Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden Baden 2021, 480 pp. (Academia Philosophical Studies, vol. 75).
S. Lisiecki, O Platonie, Arystotelesie i o sobie samym (On Plato, Aristotle and on Himself), ed. T. Mróz, Wydawnictwo Marek Derewiecki, Kęty 2021, 367 pp. (Studies and Texts in the History of Reception of Ancient Philosophy, vol. 1).

and some earlier ones…
Plato in Poland book available in OA

This post is only to announce that the book by T. Mróz, Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems (Academia Verlag/Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden Baden 2021), as a result of the agreement with the publisher, is now available free in open access on the Nomos Verlag website here and in the repository of the University of Zielona Góra, here. Enjoy!
(Another) Erasmus Teaching Visit in Vilnius
In April, 15th-19th, 2024, Tomasz Mróz enjoyed his fourth Erasmus teaching visit in Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University.

This year, some issues connected to the reception of ancient philosophy were addressed during the lecture on Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980) and his History of Philosophy. It was ancient philosophy as a subject of various problems in historiography of philosophy.

More important, however, was a talk devoted to Vitello (ca. 1230-1300) and his theoretical reflection on the nature of the daemons. Vitello’s demonology stemmed from his research in natural sciences and it employed neo-Platonic and Aristotelian elements, such as a belief in a mathematical structure of the universe, the theory of four elements and natural creatures. Vitello’s philosophical investigations were presented against the background of the 13th century developments in philosophy, especially the Averroist controversy.
Teaching duties were supplemented with meetings with the Faculty members and discussions with students extra universitatis muros. Hopefully, this was not the final chord in the co-operation between Vilnius University and the University of Zielona Góra.
AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.
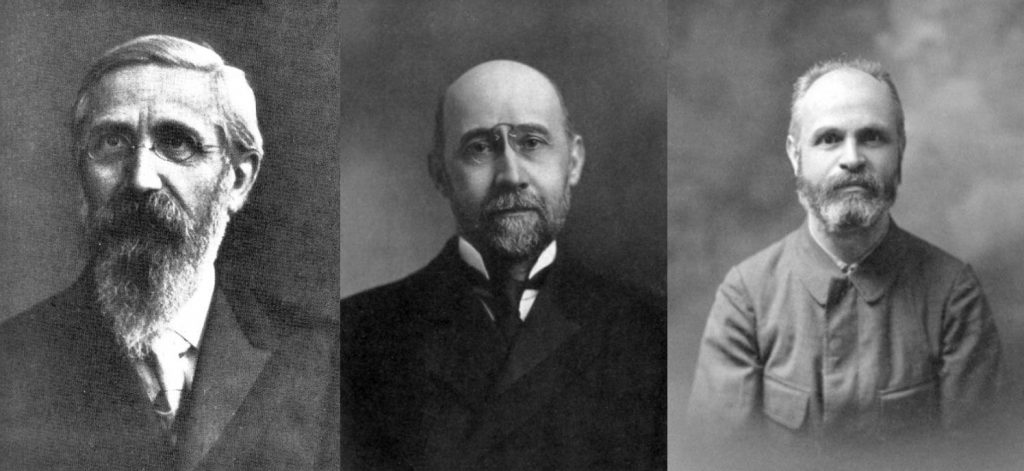

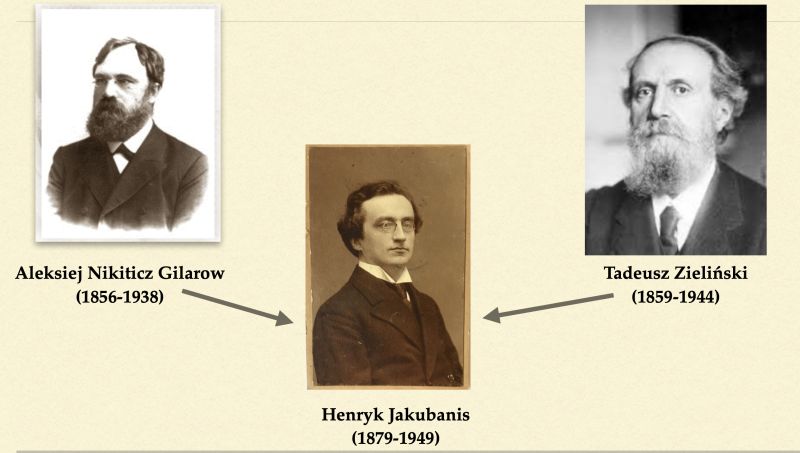
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

Recent commentaries