Home » Posts tagged 'P. Shorey'
Tag Archives: P. Shorey
A Centenary of the Kosciuszko Foundation
This year a merited institution supporting the development of Polish sciences, arts and humanities, Kosciuszko Foundation, celebrates its centennial anniversary. A decade ago Tomasz Mróz was a Kosciuszko Fellow at the University of Iowa, in the Department of Classics, whose Head at that time was Professor John Finamore.

On October 21st, 2025, in lecturing hall of the university’s library in Zielona Góra, T. Mróz delivered a talk about the history of the Kosciuszko Foundation and exchange programs for Polish scholars to pursue research visits in American academic institutions. The talk was based on the presentation provided by The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni, but its basic aim was to encourage prospective grantees to submit their project proposals and spend a couple of months in American universities. Moreover, Mróz shared his experience of preparing his proposal, of the interview and of many practical details of his 5 months research stay at the University of Iowa. The audience at the meeting was not numerous, yet highly motivated to develop their academic careers with support of the Foundation. A brief report from the meeting was published on the website of the University of Zielona Góra and on social media of the The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni.


The talk induced Mróz to recall some memories of his stay in Iowa, in the Department of Classics. Financial support from the Foundation allowed him not only to cover flights, accomodation, and daily expenses, but also to undertake a research trip to the University of Chicago and the Joseph Regenstein Library, where essential manuscript collection for his research was preserved, that is, the legacy of Paul Shorey (1857-1934), an American Plato scholar…
…and Mróz’s project was focused, not surprisingly, on the reception of Plato, that is, on the controversy between Shorey and a Polish Plato scholar, Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954), over the methods of reading Plato’s dialogues, their chronological order, etc. During his stay Mróz delivered a paper on this topic at a seminar meeting in the Department of Classics.
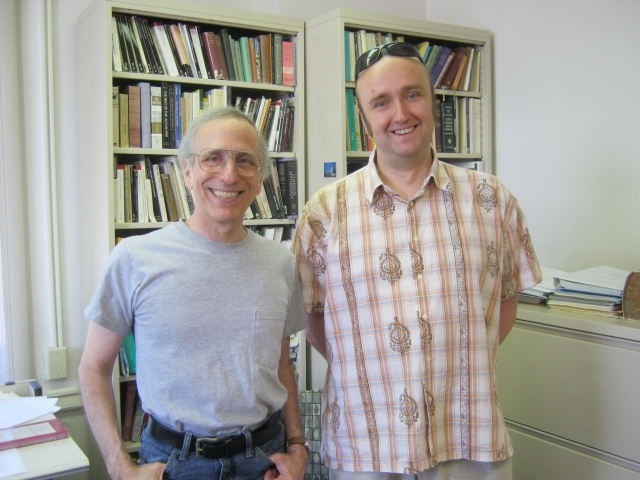


It all would not have been possible without a kind invitation from Professor John Finamore (on the left) who was at that time the Head of the Department of Classics and was very helpful for Mróz to settle in Iowa City, feel comfortable in the Department and do his research work in accordance to the plan. Thank you, John! It was a beneficial semester.
American Platonism and ISNS Dublin Conference
International Society for Neoplatonic Studies, in accordance with its name, promotes studies and academic work on Platonism, Neoplatonism and Platonic tradition broadly considered. In co-operation with various academic centres throughout the world ISNS organises annual conferences with large number of panels covering a wide spectrum of what can be called Neoplatonism. In 2024 the conference was held in Trinity College, Dublin on June 19th-23rd.

Among numerous panels of the Dublin conference there was one on the American Platonic tradition, its title was: Transcendental Echoes: Neoplatonism’s Influence on American Renaissance Thought. The aim of this panel was described by its originator, prof. Sonya Isaak, as follows: “this interdisciplinary panel endeavors to explore the dynamic intersections between Neoplatonism and American Transcendentalism, elucidating the profound philosophical, spiritual, and literary amalgamations that defined this vibrant movement in the 19th century…”. The panel had only three speakers (prof. Jay Bregman, prof. S. Isaak and T. Mróz), but it gathered many participants in the audience who wanted to learn bout the developments of Platonism in the 19th century American thought.
T. Mróz’s paper was titled Paul Shorey as a Plato Scholar and his Influences from Ralph Waldo Emerson. Shorey (1857–1934) was the most eminent and internationally recognised American Plato scholar at the turn of the 20th century. He took part in the then international disputes on interpreting Plato’s philosophy and the very methods of reading and researching the dialogues.

As an American Plato scholar, Shorey, in his works on Plato, did not avoid referring to American writers, with a particular emphasis on Emerson (1803–1882), the author of Representative Men (with a significant essay on Plato). Shorey, naturally, included Emerson in a long line of thinkers inspired by Plato, but the aim of Mróz’s paper was to focus on the influence exerted by the Transcendentalist writer and philosopher, Emerson, on the classics scholar and academic researcher, Shorey. Although he did not hold Emerson as a philosopher in high regard, there are some traits of his thinking of Plato which may be ascribed with Emersonian origins, for example, reading Plato as a moral philosopher and tendency toward unity. Thus the connection between American Transcendentalist movement and academic studies on Plato in American tradition was demonstrated.
Plato in Poland book available in OA

This post is only to announce that the book by T. Mróz, Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems (Academia Verlag/Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden Baden 2021), as a result of the agreement with the publisher, is now available free in open access on the Nomos Verlag website here and in the repository of the University of Zielona Góra, here. Enjoy!
AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.
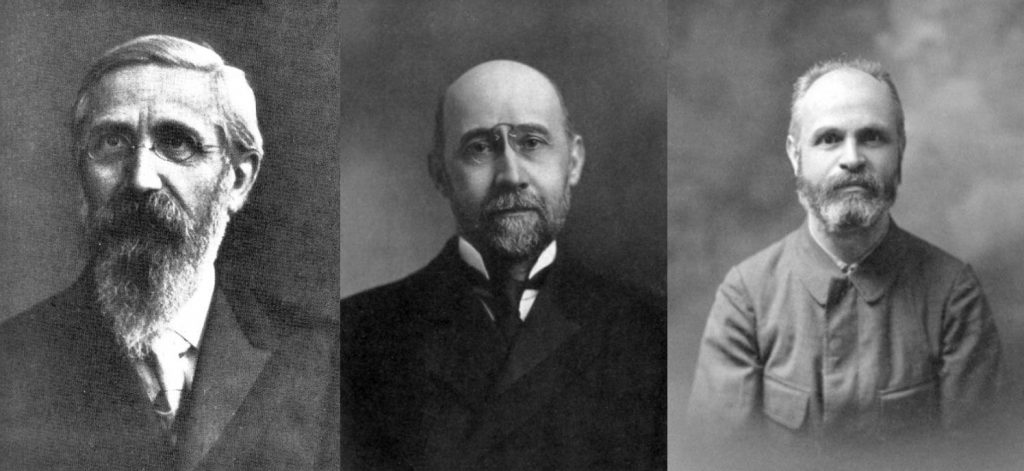

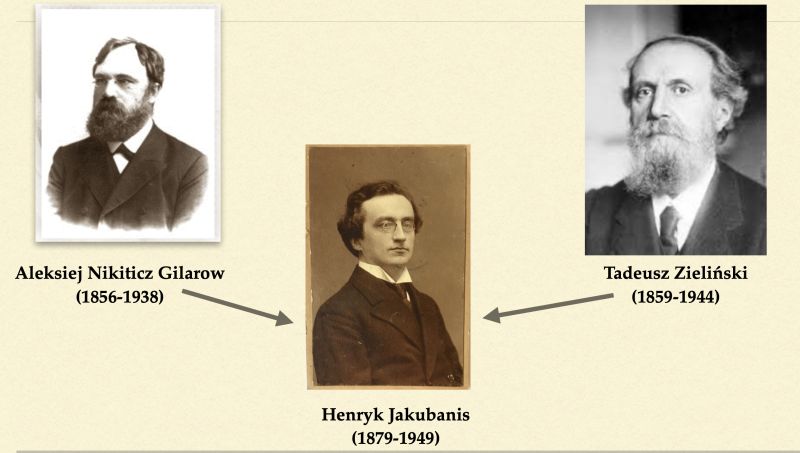
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

20th Annual Conference of the International Society for Neoplatonic Studies
International Society for Neoplatonic Studies (ISNS) has for decades been a forum for scholars researching various phaenomena in the history of Neoplatonism, including even the latest developments of the reception of Platonism. In June 14th-17th, 2023, ISNS conference was held at the foot of Etna, in Catania, in co-operation with Università degli Studi di Catania.
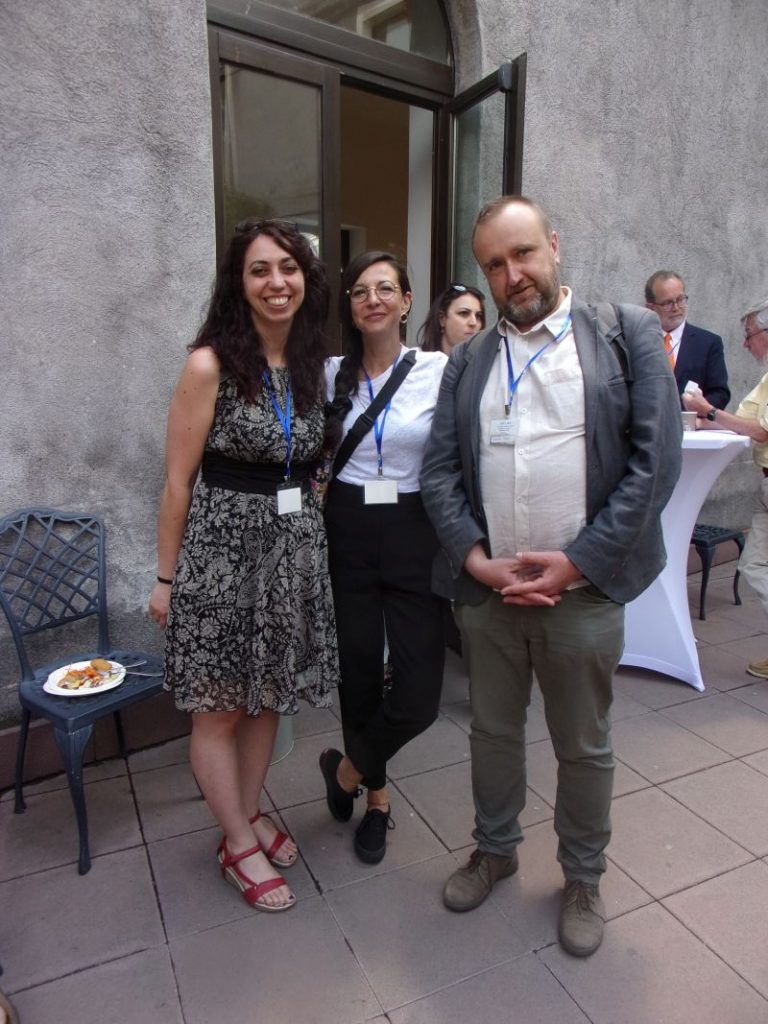


One of the numerous panels at the conference was devoted to Plato’s Timaeus, the concept of time and its influence on various thinkers across the history of philosophy up to recent times. The panel was organised by the two professors, Laura Marongiu and Laura Follesa, both of University of Milan. Although this panel focused on relatively narrow topic, the response from scholars was impressive and thus the list of speakers in this successful panel demonstrated incessant interest of generations of scholars in the Timaeus, the late dialogue of Plato. The topics ranged from Speusippus, Aristotle, Xenocrates, Numenius, Plotinus, Iamblichus, Proclus, Simplicius and Philoponus to M. Ficino, L. Bruno, F.W.J. Schelling, G.W.F. Hegel, H. Bergson and E. Husserl (on the photo: L. Follesa, L. Marongiu & T. Mróz).
T. Mróz presented a paper titled The Timaeus and Three Scholars of One Generation: P. Natorp, P. Shorey and W. Lutosławski. Mróz discussed various interpretations of the Timaeus by the three scholars, focusing on their general methods in reading Plato and their views on Plato’s concept of the time, although none of them considered the time to be the central issue in the dialogue.

ISNS conferences have always been a forum for scholars who explore various aspects of Platonism, Neoplatonism and Plato reception from antiquity up to contemporary times. Professor John Finamore, spiritus movens of all of ISNS symposia, spares no efforts to hold ISNS events in various academic centres and to provide opportunity for scholars throughout the world to take part in them. He has recently announced that next year’s ISNS conference will take place in Dublin, in co-operation with Trinity College.
Lewis Campbell and His International Connections

Studia Historiae Scientiarum, an annual journal published by Polish Academy of Arts and Sciences, includes a section Science beyond Borders. In 2018 a paper by Tomasz Mróz was published there on Lewis Campbell’s (1830–1908) correspondence held in Peterhouse Library, Cambridge.
The paper presents L. Campbell, his research on Plato, and the collection of letters sent to this Scottish scholar by: James Martineau (1805–1900), William Hepworth Thompson (1810–1886), Paul Shorey (1857–1934), Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), Eduard Gottlob Zeller (1814–1908), Franz Susemihl (1826–1901), and Theodor Gomperz (1832–1912). This collection supplements the knowledge of the research on Plato’s dialogues at the turn of the 20th century, since Plato scholars in their letters touched on the issues relating to the methods and results of the research on the chronology of Plato’s dialogues. They made judgements concerning the works of other academics, they sent to each other their own publications, and reported on the progress of their studies. They also did not shy away from making personal remarks and communicating personal reflections.
Publishing this paper was preceded by a research stay in Cambridge in June and July 2016, which was sponsored by Lanckoroński Foundation. Additionally, archival materials from St Andrews University Library (Special Collections) supplemented the whole work.
The paper in Polish is available on the journal’s website here.
A View of Plato’s Paths in Poland

A lengthy, 480 pages, monograph book by T. Mróz was published in Academia Verlag’s series “Academia Philosophical Studies” as vol. 75. The title of the book is Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems.
Some material from the book, including table of contents, is available on publisher’s website. The book attempts to make Polish Plato reception available to non-Polish readers. The years 1800-1950 cover essential phaenomena in modern Polish philosophy, for they encompass periods of reception of Western philosophical trends and the development of the Lvov-Warsaw school, neo-Messianism and neo-Scholasticism. The book discusses how each of these phaenomena contributed to interpreting Plato. The material is divided into three main parts focused on various types of reception.
The book is a final outcome of a project sponsored by Polish government within the National Programme for the Development of Humanities funding scheme. An essential collaborator in this project was Una Maclean-Hańćkowiak, who patiently edited the author’s style.
Recent commentaries