Home » Posts tagged 'Germany'
Tag Archives: Germany
Plato in Poland book available in OA

This post is only to announce that the book by T. Mróz, Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems (Academia Verlag/Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden Baden 2021), as a result of the agreement with the publisher, is now available free in open access on the Nomos Verlag website here and in the repository of the University of Zielona Góra, here. Enjoy!
“Oral History and the Classics” Team in Poznań
On Dec. 5th, 2023, Oral History and the Classics project team enjoyed the honour to visit Professor Marian Andrzej Wesoły at his home, in the vicinity of Poznań. Prof. Wesoły agreed to give an interview which will be included in the Oral History and the Classics collection on the website of the University of Hradec Králové.
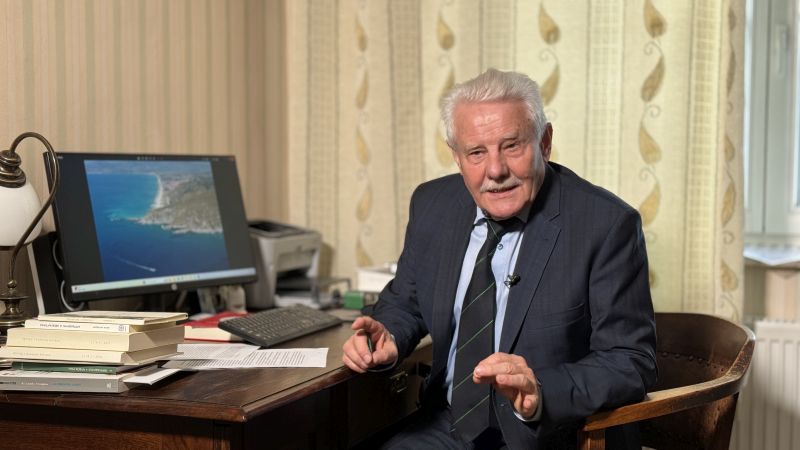

Marian Wesoły is currently a professor emeritus of Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań and lectures at the Jacob of Paradies Academia in Gorzów Wielkopolski. His entire academic career in Poland was connected to Poznań and Adam Mickiewicz University. His doctoral (1977) and postdoctoral (1992) dissertations were devoted to the history of Greek philosophy. In 2008 he received the title of a full professor. He was granted several foreign scholarships, e.g. in Italy (1980: University of Padova, 1983: Italian Institute for History in Naples, 1997: Villa I Tatti), Germany (1986/87: University of Tübingen), and Greece (1993, 2000, 2012: Academy of Athens). Prof. Wesoły is a co-founder of the „Peitho. Examina Antiqua” journal. For 20 years he has regularly participated in the Eleatica-Symposia, initiated by Prof. Livio Rossetti at the Alario Foundation in Ascea, close to the ruins of ancient Elea/Velia. Finally, we should mention that on the 100th anniversary of the Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań (2019) he was awarded Knight’s Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta.

Prof. Wesoły is a specialist in Greco-Roman and Byzantine philosophies. In his numerous works he attempts to combine philological analyses with philosophical interpretation. Moreover, he is active as a translator and one of his most recent productions is a bilingual edition and commentary of Aristotle’s Analytica Priora et Posteriora (2020).
During the interview prof. Wesoły reflected on his academic and research curriculum, but also shared his views on perspectives of his discipline, on political constraints in researching ancient philosophy, recalled his memories of the great scholars whom had the opportunity to meet and with whom he collaborated etc. When the whole recording is edited and furnished with English subtitles, it will be make public and available on the project’s website.
The interview meeting with prof. Wesoły would not be possible without his kind consent and warm welcome of the team members by his family at their home. Those were Tomasz Mróz and Jaroslav Daneš who carried out the interview, while Jan Kadeřábek, a cinematographer and a cameraman, took care of all the technicalities.

AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

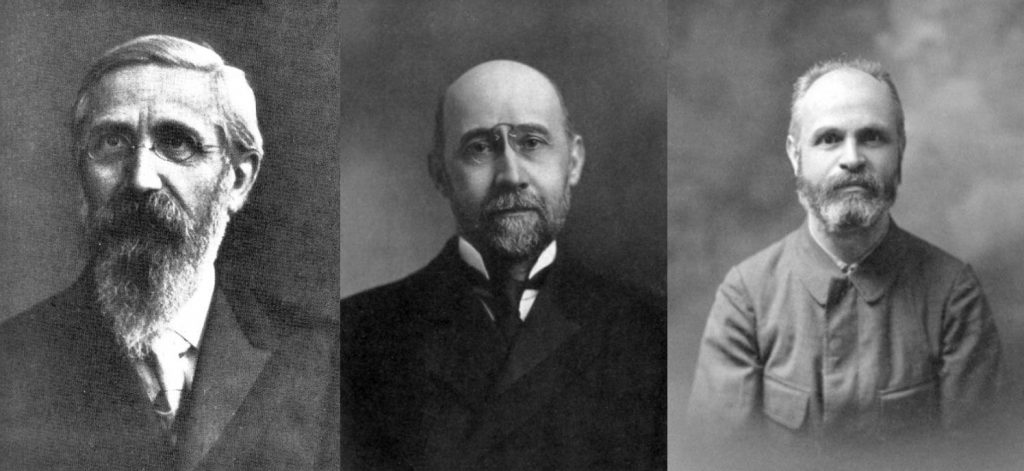
T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.

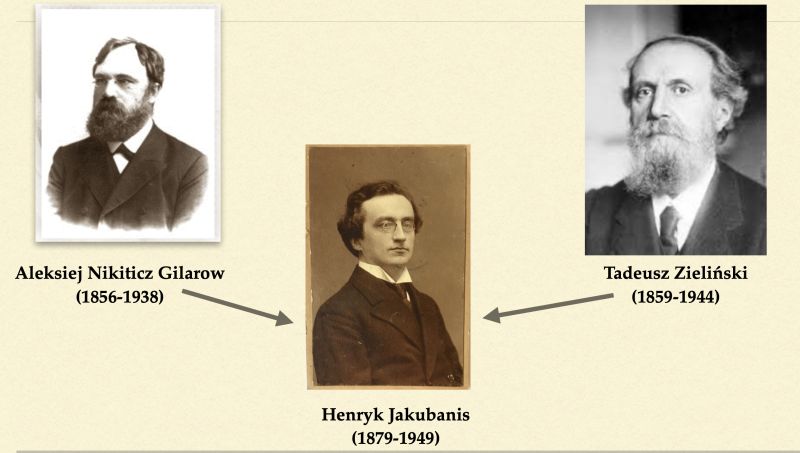
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

A Member of AΦR Received a NAWA Scholarship

Mariam Sargsyan, already a member of the AΦR research group and a grantee in National Science Centre (NCN) project on Henryk Jakubanis (Генрих Якубанис: 1879–1949) and his works on ancient Greek philosophy, has recently received a scholarship from NAWA (Polish National Agency for Academic Exchange). The programme’s name is NAWA Preludium Bis 2 and it is intended exclusively for doctoral students working under NCN projects in doctoral schools. The aim of NAWA Preludium Bis 2 programme is to support international mobility of doctoral students by enabling them to gain academic experience in international research centres.

Considering the topic of M. Sargsyan’s dissertation, H. Jakubanis, a scholar whose career started successfully in Saint Vladimir Imperial University of Kyiv, at first she intended to spend her internship in Kyiv, in Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv. After the Russian invasion on Ukraine, unfortunately, her research stay there turned out to be impossible.
In these circumstances the plans had to change and eventually M. Sargsyan’s scholarship will be spent in Germany, at the Martin Luther University in Halle, and to be more precise, at the Aleksander Brückner Centre for Polish Studies (ABZ), from April to July 2023. Scholars connected to ABZ research both historical and present-day developments in Polish politics, society, language, and culture in multidisciplinary perspective. Professor Yvonne Kleinmann, who is the Head of ABZ, agreed to be an academic supervisor of M. Sargsyan’s scholarship.
The main goal of M. Sargsyan’s internship is to research historical and cultural circumstances of Jakubanis’ life and to enrich her thesis with literature hardly available in Poland. It will significantly contribute to producing a comprehensive biographical, historical and philosophical study of this historian of philosophy.
The list of M. Sargsyan’s tasks in Halle includes: preparation and presentation of a paper at the Colloquium of East-European History (Interdisziplinäres Kolloquium Osteuropäische Geschichte / Polenstudien) and participation in the activities of ABZ.

A Paper on Vilnius’ Plato Scholar in a Lithuanian Journal

In “Logos” (issue 112), a Lithuanian journal, a paper was published on Józef Jeżowski (1793-1855) and his assessment of a Russian translation of Plato’s Laws. Subtitle of the paper, Classics scholar from Vilnius and his Plato between Germany and Russia, or Italy and Lapland, stems from Jeżowski’s deliberations on the future of classical and Platonic studies on the outskirts of Europe.

Who was Jeżowski? A partly forgotten figure among excellent scholars in the humanities, who were affiliated to Vilnius University in the first decades of the 19th century, an expert in classical languages and literatures, a scholar recognised for his edition of Horace’s Odes, an outstanding student of G. E. Grodek, moreover, a founding member of the Philomath Society, and a friend of A. Mickiewicz. Considering today’s political borders, his life’s path encompassed three countries, Lithuania, Russia and Ukraine, though in the 19th century Jeżowski was a Pole and a citizen of Russian Empire.
In a word, Jeżowski’s assessment of a translation of Plato’s Laws, produced by a Russian scholar, V. Obolensky, was not favourable, though somewhat superficial. Jeżowski, however, was rather focused on expressing his neo-classical manifesto rather than on a fair and insightful evaluation of the Russian text. His work bore a long title, which could be translated as follows: On the Progress of Philological Research Concerning the Writings of Plato. A Critical Piece, Composed Due to a Publication of the “Dialoues on the Laws”, Attributed to Plato. This study was actually addressed to Polish reading audiences, yet it was published in Moscow in 1829, during his years of exile in Russia. Jeżowski’s most important argument in his criticism was a complete lack of Obolensky’s references to German scholars, whose merits were considered by Jeżowski too significant to be passed over in silence. In his criticism, he was nevertheless optimistic, hoping that even in the most inhospitable circumstances it is possible for the humanities to flourish, and hard work can transform Lapland-like academic desert of Russia into blossoming Italy-like scenery, to which he compared German scholarship.
Considering the fact that Jeżowski was born in Uman and died in vicinity of Kaniv, both places being located in today’s Ukraine, and considering present war, Russian aggression on Ukraine, the paper was dedicated by the author to his fellow Ukrainian historians of philosophy.
A View of Plato’s Paths in Poland

A lengthy, 480 pages, monograph book by T. Mróz was published in Academia Verlag’s series “Academia Philosophical Studies” as vol. 75. The title of the book is Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems.
Some material from the book, including table of contents, is available on publisher’s website. The book attempts to make Polish Plato reception available to non-Polish readers. The years 1800-1950 cover essential phaenomena in modern Polish philosophy, for they encompass periods of reception of Western philosophical trends and the development of the Lvov-Warsaw school, neo-Messianism and neo-Scholasticism. The book discusses how each of these phaenomena contributed to interpreting Plato. The material is divided into three main parts focused on various types of reception.
The book is a final outcome of a project sponsored by Polish government within the National Programme for the Development of Humanities funding scheme. An essential collaborator in this project was Una Maclean-Hańćkowiak, who patiently edited the author’s style.
Recent commentaries