Home » Posts tagged 'In Polish'
Tag Archives: In Polish
The Interview with Professor Marian Wesoły Available with English Subtitles
We are very glad to announce that finally, after two years, the interview with Professor Marian Wesoły is available online with English subtitles on the website of the project Oral History and the Classics, here. We have already reported on shooting this interview here.

Professor Wesoły, at his desk at home, talked about his intellectual biography, his teachers, collaborators, colleagues, correspondents, about his academic adventures at research centres in Germany (Tübingen) and Italy (Naples), books and editions, and many other fascinating issues. Moreover, he shared his views on prospective developments of research in the field of ancient philosophy.
We want to encourage you, once again, to click here and watch the video.
The Ceremony of Presenting Doctoral Diplomas
In 2025 there were many important moments for the AΦR group, but one of the most remarkable of them took place on November the 20th. It was the ceremony of presenting the new doctors with their diplomas. The members of the AΦR group took part in such an event for the first time.
The degree holder was Mariam Sargsyan, (now Ph.D.!), who – after taking a traditional doctoral oath in Latin to the Rector Magnificus of the University of Zielona Góra, prof. dr hab. Wojciech Strzyżewski – was officially granted the doctoral title cum laude and the diploma by her academic supervisor, dr hab. Tomasz Mróz.
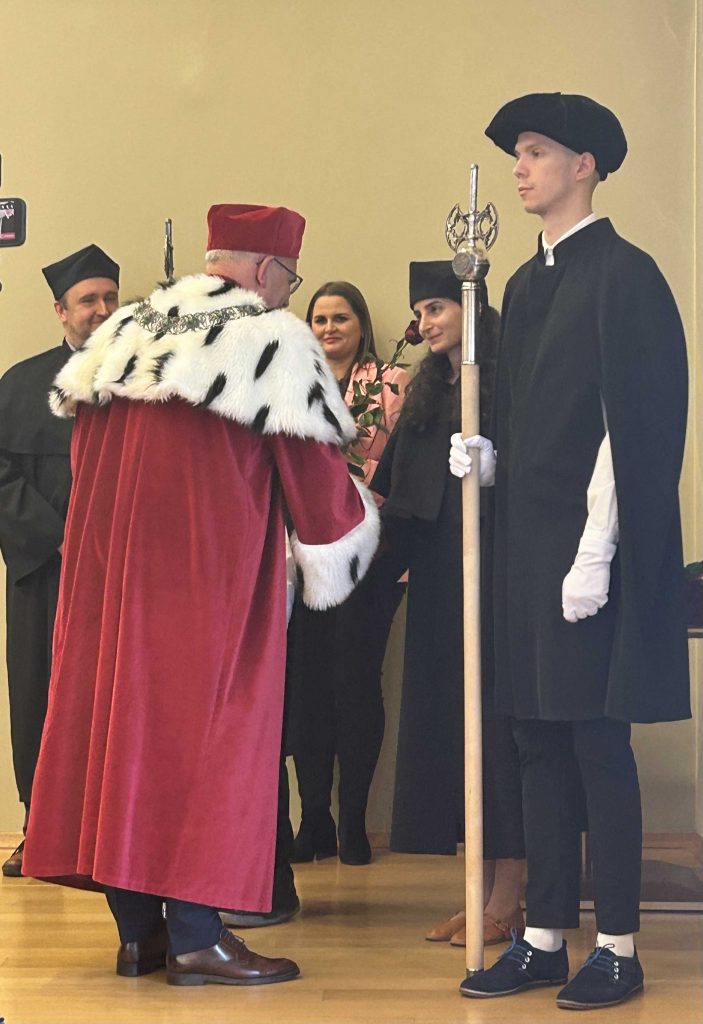

Some details of Sargsyan’s thesis and a report from her public defence can be found here, while all the information about the projects in which she participated, her activities and achievements can be found on our website tagged with M. Sargsyan or H. Jakubanis, whose life and works were the subject of her dissertation.
A full account of the ceremony on the university’s website, in Polish, can be found here.
Congratulations!
Philosophy in Zielona Góra. An Anniversary
This year, Institute of Philosophy, University of Zielona Góra (UZ), where Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group is affiliated, celebrates its 30th anniversary. Among the variety of events, there was a conference on 23rd-24th October, devoted to the problem of co-operation in its various relations to theory, history and philosophical practice. AΦR’s history at UZ is obviously much shorter, but two of its representatives actively participated in the conference.

Mariam Sargsyan was the first of them. In her presentation she discussed the results of her doctoral studies at UZ and her dissertation, successfully defended earlier this year. She focused on analyses of Henryk Jakubanis’ (1879-1949) historical-philosophical legacy, which consists of three main parts: 1) his work on Empedocles and its methodology; 2) Plato in his (partly unpublished) writings; 3) his views on ancient and modern ways of doing philosophy. Moreover, Sargsyan presented the conclusions of her research on intellectual genealogy of Jakubanis’ thought.
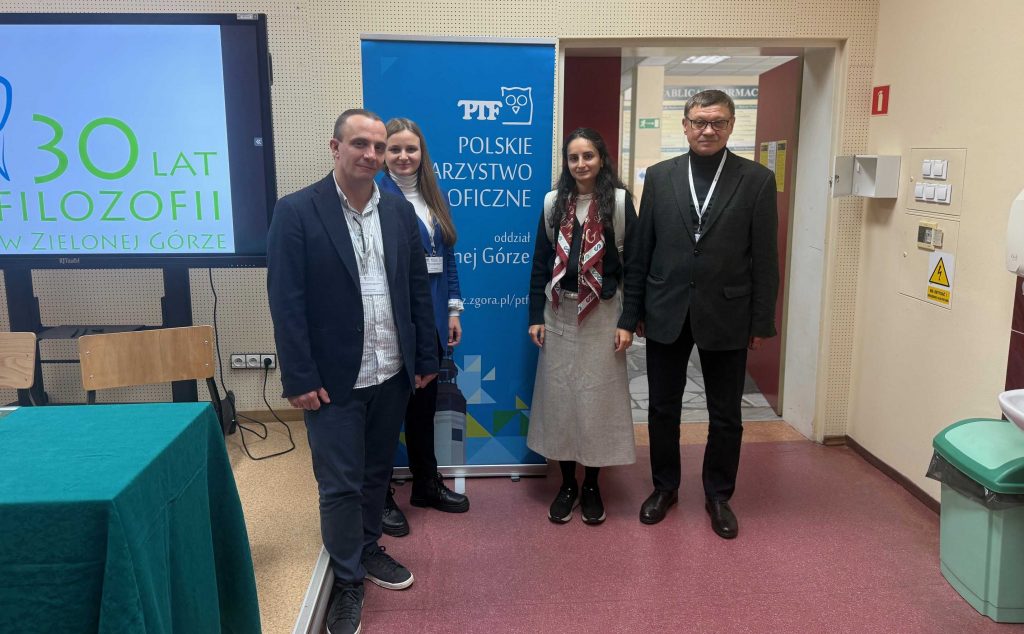

What was even more significant was the fact that Ukrainian participants (see the photo above) of the conference, who work at the National University of Kyiv, attended Sargsyan’s presentation on Jakubanis, who had studied and worked in Kyiv a century ago. They were very interested in her results and provided valuable feedback that could be helpful in improving the text of her doctoral thesis before it is published. The discussion between them demonstrated how important it is to confront different points of view on one subject which is researched by scholars from different countries, applying various methods and interested in different aspects of the history of philosophy.
The second conference participant from AΦR was Adrian Habura who delivered a paper on Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980) and his reflection on social aspects of human happiness. Habura discussed Tatarkiewicz’s definition of happiness and his understanding of human life, then he examined the role of the others in individual happiness and the links between human individual and society in their relations to happiness. In his paper Habura developed a general view on the role of society in Tatarkiewicz’s philosophical and ethical considerations contained in his book Analysis of Happiness.
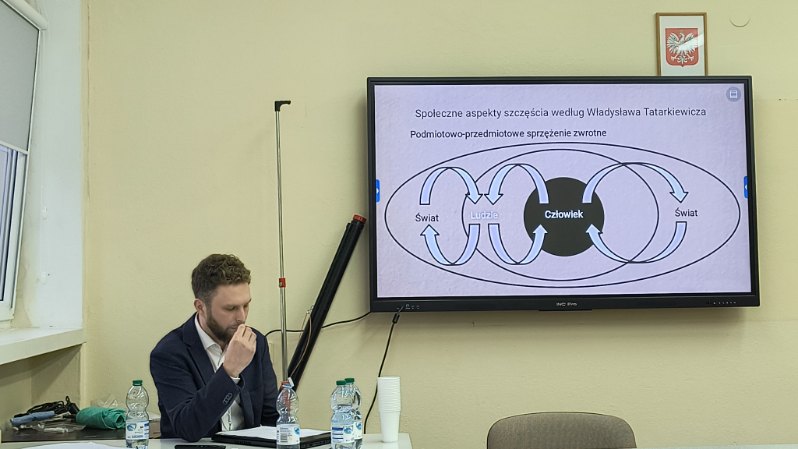
Although Habura’s paper was not directly devoted to the reception of ancient philosophy in Tatarkiewicz’s writings, the following discussion allowed him to address this issue. He highlighted some similarities and differences between Aristotle’s and Tatarkiewicz’s understandings of happiness and convincingly demonstrated how Aristotle could have inspired ethical investigations of this Polish philosopher, whose doctoral thesis on Aristotle was composed under supervision of the Marburg neo-Kantians.
A Centenary of the Kosciuszko Foundation
This year a merited institution supporting the development of Polish sciences, arts and humanities, Kosciuszko Foundation, celebrates its centennial anniversary. A decade ago Tomasz Mróz was a Kosciuszko Fellow at the University of Iowa, in the Department of Classics, whose Head at that time was Professor John Finamore.

On October 21st, 2025, in lecturing hall of the university’s library in Zielona Góra, T. Mróz delivered a talk about the history of the Kosciuszko Foundation and exchange programs for Polish scholars to pursue research visits in American academic institutions. The talk was based on the presentation provided by The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni, but its basic aim was to encourage prospective grantees to submit their project proposals and spend a couple of months in American universities. Moreover, Mróz shared his experience of preparing his proposal, of the interview and of many practical details of his 5 months research stay at the University of Iowa. The audience at the meeting was not numerous, yet highly motivated to develop their academic careers with support of the Foundation. A brief report from the meeting was published on the website of the University of Zielona Góra and on social media of the The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni.


The talk induced Mróz to recall some memories of his stay in Iowa, in the Department of Classics. Financial support from the Foundation allowed him not only to cover flights, accomodation, and daily expenses, but also to undertake a research trip to the University of Chicago and the Joseph Regenstein Library, where essential manuscript collection for his research was preserved, that is, the legacy of Paul Shorey (1857-1934), an American Plato scholar…
…and Mróz’s project was focused, not surprisingly, on the reception of Plato, that is, on the controversy between Shorey and a Polish Plato scholar, Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954), over the methods of reading Plato’s dialogues, their chronological order, etc. During his stay Mróz delivered a paper on this topic at a seminar meeting in the Department of Classics.
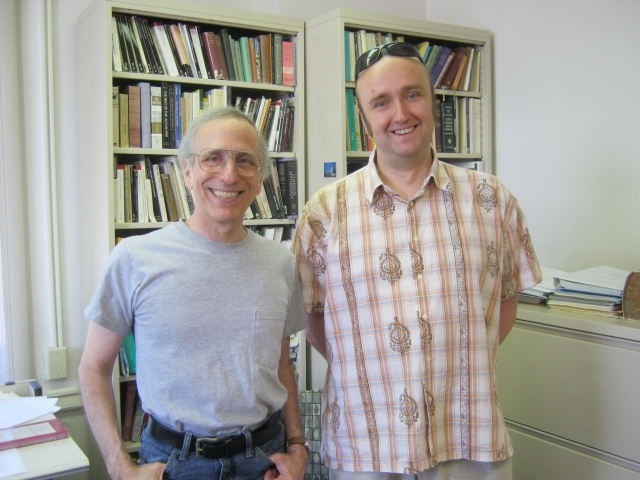


It all would not have been possible without a kind invitation from Professor John Finamore (on the left) who was at that time the Head of the Department of Classics and was very helpful for Mróz to settle in Iowa City, feel comfortable in the Department and do his research work in accordance to the plan. Thank you, John! It was a beneficial semester.
The First Doctoral Degree by a Member of AΦR Team
On June 24th, 2025, a public defense of Mariam Sargsyan’s (Մարիամ Սարգսյան) doctoral thesis took place in the Institute of Philosophy, University of Zielona Góra (UZ). The title of her dissertation was Henryk Jakubanis (1879–1949) as a Researcher of Ancient Philosophy and Its Reception. The whole event was chaired by prof. Jacek Uglik and it proceeded in accordance with a regular schedule. At the start he curriculum of the candidate was presented by the supervisor, T. Mróz, who stressed the fact that M. Sargsyan was the first international student in the Doctoral School for Humanities and Social Sciences, and the only beneficiary of the research project NCN Preludium bis (with T. Mróz as a PI) and NAWA Preludium bis in the history of UZ.

Then M. Sargsyan took the floor and delineated the main points of her thesis which aimed at providing a synthetic study of H. Jakubanis as a researcher of ancient philosophy. Her study included a discussion of less-known aspects of H. Jakubanis’ life and work, in particular his academic positions in Kyiv; an analysis of his interpretations of selected Greek philosophers (Empedocles and Plato); and an examination of his methods etc.
A particular emphasis was put on the significance of his national sentiments and identity in motivating his decisions and shaping his career path; and on his contribution to the development of research in ancient philosophy and promotion of Polish culture in Kyiv in the early 20th century and subsequently in Lublin during the interwar period. The second part of the presentation was focused on H. Jakubanis scholarly achievements. His works were divided into three groups: 1) a monograph and translation of Empedocles (1906); 2) various studies on Plato and reception of Platonism, including an incomplete manuscript of his final university thesis (1900); 3) works promoting the value of ancient philosophy for general audiences, not only scholars, in the modern age.
One of the most significant results of Sargsyan’s dissertation was an identification three key influences in Jakubanis’ intellectual genealogy. They were: 1) his supervisor, Alexei Gilarov (1856-1938), whose role in forming Jakubanis’ biographical-genetic method and his interpretation of Plato was crucial; 2) Tadeusz Zieliński (1859-1944) and his conviction in the importance of the ancient legacy for modern culture; 3) the works by Eduard Zeller (1814-1908), which exerted impact on Jakubanis’ views on Empedocles and Plato.

On the whole, as Sargsyan’s dissertation demonstrates, Jakubanis was a historian of ancient thought, with a good background in classical languages, whose primary goal as a lecturer and scholar was to promote ancient thought. Contrary to his methods that can be considered today as outdated, his translation of Empedocles’ fragments still circulates in the Russian-speaking world and seems to be his lasting contribution to disseminating Greek philosophy.
The dissertation was assessed by three reviewers, they were prof. Zbigniew Nerczuk (Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń), prof. Steffen Huber (Jagiellonian University), and prof. Wiesława Sajdek (Jan Długosz University in Częstochowa). They all were present to read out loud their positive reviews and ask a couple of questions. They were particularly concerned with some ambiguities in Sargsyan’s account of Jakubanis’ career and academic titles he had obtained, since not all the documents have been preserved. Another key issue concerned some lacking points in broader historical and philosophical context of Jakubanis’ views, as Sargsyan preferred to focus on the direct impact exerted on him by the scholars he had referred to or collaborated with.

Finally, after hearing the reviews, questions and answers, the commission decided to award M. Sargsyan with a doctoral degree cum laude. Her dissertation has, no doubt, broadened and deepend the knowledge of the reception of ancient philosophy in Central and Eastern Europe in general, and of Henryk Jakubanis, a scholar writing on history of philosophy, who left his mark on the intellectual life in Poland, Ukraine and Russia, in particular.
After her successful doctoral defence M. Sargsyan returned to Armenia, her homeland, but we all hope here for further collaboration and for funding opportunities to publish her dissertation.
Dear Doctor Sargsyan!
Good luck with your research plans and see you back soon!
Ancient Φilosophy Reception at the 12th Seminar of Historians of Polish Philosophy

Seminar of Historians of Polish Philosophy (SHPPh) is a cyclical academic event held at various universities in Poland since its first edition in Warsaw in 2006. In 2025 (May 19th-20th), it was for the first time at the University of Zielona Góra (UZ) where Polish researchers of their native philosophical traditions gathered. Central topic of this edition of SHPPh was the problem of classical thinkers and epigons in the development of Polish thought. Detailed programme of the whole event can be downloaded here.
The seminar was also an opportunity to celebrate the second edition of the book Classics of Polish Philosophy by Ryszard Palacz, an essential figure for historians of philosophy at UZ, and a researcher of reception of Greek philosophy in medieaval thought, about whose passing we have informed in the autumn of 2024. Full program of the event can be downloaded here and a brief report (in Polish) on the UZ’s website can be found here (with a photo gallery). The seminar was accompanied by an exhibition devoted to Professor Palacz and many speakers referred to his work and his understanding of classical Polish philosophers.


Two AΦR group members delivered their papers during the SHPPh. Tomasz Mróz talked about Bohdan Kieszkowski (1903-1997) and about Polish and international disputes on his works on Florentine Platonism.
In the thirties in Poland Kieszkowski was engaged in a dispute with Marian Heitzman (1899-1964), who accused him of underestimating the influences of medieval neoplatonism on Ficino. Heitzman and Kieszkowski, two scholars of one generation, two researchers of Renaissance Platonism, represented two different academic centres, conservative Cracow and more progressive Warsaw, and their polemical texts were published separately in philosophical journals in Cracow (Heitzman) and Warsaw (Kieszkowski). Kieszkowski, naturally, considered Heitzman’s position to be an overestimation of medieval influences on Renaissance’s thought and labelled it as ‘medievalism’. On international niveau a polemic against Kieszkowski’s work came from a Portuguese scholar, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010), who praised Kieszkowski’s scholarship, yet spared no words of criticism against Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico della Mirandola’s Conclusiones (Geneve 1973).
Adrian Habura’s talk smoothly concluded the whole conference focusing, on the one hand, on a paper titled Four Understandings of Classicism by Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980), and on the other hand, on Palacz’s (1935-2024) arguments for including Tatarkiewicz among the classics of Polish philosophy.

Habura analysed Tatarkiewicz’s notion of classicism and supplemented Palacz’s arguments for including Tatarkiewicz among the classics, demonstrating that not only his History of Philosophy, History of Aesthetics, and History of Six Ideas, that is, basically historical studies, but also his Analysis of Happiness, the original philosophical work by Tatarkiewicz, bears the mark of classic. Ethical considerations in the Analysis of Happiness, noticeably influenced by Aristotle, not to mention Tatarkiewicz’s doctoral degree from Marburg on a thesis devoted to Aristotle, allowed Habura to highlight an additional aspect of Tatarkiewicz as a classic, for he was not only a classic among Polish philosophers, but also a classic in another understanding: as a follower or – to use the term proposed by Juliusz Domański – a user of Aristotelian philosophy. And it was Aristotle whom Tatarkiewicz himself regarded as the most classical among all the classical philosophers of ancient Greece.
H. Jakubanis’ Empedocles in OA

Last year we announced publishing Polish translation of a Russian study by Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949), originally published in Kyiv over a century ago, Empedocles: a Philosopher, a Doctor and a Magus, therefore there is no need to repeat all the information here. Suffice to say that the text was translated by Mariam Sargsyan and Adrian Habura, and the whole volume ends with an afterword by Katarzyna Kołakowska, a contemporary Polish expert on Empedocles.
The book can be purchased on the publisher’s website here. We are now, however, glad to inform that it is available in OA, via online repository of the University of Zielona Góra.
Recent commentaries