Home » Posts tagged 'Vilnius' (Page 2)
Tag Archives: Vilnius
“Small Grant” from the University of Zielona Góra

Prof. Marcin Mrugalski, the Deputy Rector for Science and International Cooperationof of the University of Zielona Góra (UZ), home institution of the AΦR, awarded Tomasz Mróz with a “Small Grant” of a maximum possible value. These internal grants are distributed by the Rector annually among those researchers of UZ, who had submitted their proposals to the National Science Centre (NCN), received positive assessements from the experts, yet finally had not been granted funding. Aim of the “Small Grants” is to increase the chances of the researches in future granting competitions.
“Small Grant” funds for AΦR will be spent on developing and strenghtening a co-operation between AΦR members and the Institute of Philosophy (UZ) with colleagues from the Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University (VU), on the topic of the history of research on ancient philosophy in VU during its complex history.

Erasmus Teaching Visit in Vilnius University
In April, 18th-22nd, 2023, Tomasz Mróz enjoyed his third Erasmus teaching visit in Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University.

Vilnius University is a unique research and teaching institution in Central-Eastern Europe. It has a long and sometimes turbulent Polish-Lithuanian history. Some of the lectures delivered by T. Mróz to philosophy students in Vilnius concerned a part of this history and, naturally, reception of ancient philosophy.
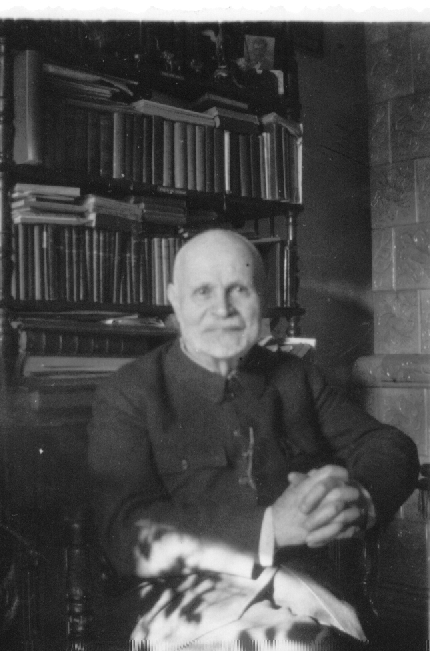
One of the lectures discussing the issues of ancient philosophy reception had Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954) as its topic. The focus was on his Vilnius period and his vision of a philosophical development of Plato from idealism to spiritualism. Since Lutosławski considered Polish Romantic Messianism to be founded on spiritualism, consequently he could consider this unique tradition to be rooted in Plato, who was presented by Lutosławski as an ancient philosophical predecessor of Polish 19th century literary and philosophical tendency.
Another lecture in which ancient philosophy reception appeared was devoted to Vitello (ca. 1230-1300?) and his theoretical reflection on the nature of the daemons. Vitello’s demonology stemmed from his research in natural sciences and it employed neo-Platonic and Aristotelian elements, such as a belief in a mathematical structure of the universe and the theory of four elements. Vitello’s philosophical investigations were presented against the background of the 13th century developments in philosophy.

Teaching duties were supplemented with meetings with the Faculty members and discussions on the plans of a future co-operation activities between philosophers of Vilnius University and University of Zielona Góra.
A Paper on Vilnius’ Plato Scholar in a Lithuanian Journal

In “Logos” (issue 112), a Lithuanian journal, a paper was published on Józef Jeżowski (1793-1855) and his assessment of a Russian translation of Plato’s Laws. Subtitle of the paper, Classics scholar from Vilnius and his Plato between Germany and Russia, or Italy and Lapland, stems from Jeżowski’s deliberations on the future of classical and Platonic studies on the outskirts of Europe.

Who was Jeżowski? A partly forgotten figure among excellent scholars in the humanities, who were affiliated to Vilnius University in the first decades of the 19th century, an expert in classical languages and literatures, a scholar recognised for his edition of Horace’s Odes, an outstanding student of G. E. Grodek, moreover, a founding member of the Philomath Society, and a friend of A. Mickiewicz. Considering today’s political borders, his life’s path encompassed three countries, Lithuania, Russia and Ukraine, though in the 19th century Jeżowski was a Pole and a citizen of Russian Empire.
In a word, Jeżowski’s assessment of a translation of Plato’s Laws, produced by a Russian scholar, V. Obolensky, was not favourable, though somewhat superficial. Jeżowski, however, was rather focused on expressing his neo-classical manifesto rather than on a fair and insightful evaluation of the Russian text. His work bore a long title, which could be translated as follows: On the Progress of Philological Research Concerning the Writings of Plato. A Critical Piece, Composed Due to a Publication of the “Dialoues on the Laws”, Attributed to Plato. This study was actually addressed to Polish reading audiences, yet it was published in Moscow in 1829, during his years of exile in Russia. Jeżowski’s most important argument in his criticism was a complete lack of Obolensky’s references to German scholars, whose merits were considered by Jeżowski too significant to be passed over in silence. In his criticism, he was nevertheless optimistic, hoping that even in the most inhospitable circumstances it is possible for the humanities to flourish, and hard work can transform Lapland-like academic desert of Russia into blossoming Italy-like scenery, to which he compared German scholarship.
Considering the fact that Jeżowski was born in Uman and died in vicinity of Kaniv, both places being located in today’s Ukraine, and considering present war, Russian aggression on Ukraine, the paper was dedicated by the author to his fellow Ukrainian historians of philosophy.
Recent commentaries