Home » Posts tagged '2025'
Tag Archives: 2025
Full Professorship for Tomasz Mróz
We are very glad to announce that Tomasz Mróz, the Head and Initiatior of the Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group at the University of Zielona Góra (Institute of Philosophy), was granted the title of the professor (or full professor, professor ordinarius), the highest academic rank in Poland, by the President of the Republic of Poland, Karol Nawrocki, in December 2025. The ceremony of presenting the nominations to the new professors took place in the Presidential Palace in Warsaw, official residence of the Polish head of the state, on January 7th, 2026.

The whole procedure of obtaining the professorship took almost a year. All the necessary documents were submitted to the Council of Academic Excellence (CAE) in January 2025. CAE appointed five referees to assess quantity and quality of T. Mróz’s scholarly achievements and his entire academic curriculum. The referees were professors: Krzysztof Brzechczyn, Mikołaj Domaradzki, Janina Gajda-Krynicka, Jerzy Kojkoł and Andrzej Wawrzynowicz. After receiving five positive opinions, CAE, at a session in September 2025, unanimously passed a motion to the President to grant the professor title to T. Mróz.
Congratulations!
The Interview with Professor Marian Wesoły Available with English Subtitles
We are very glad to announce that finally, after two years, the interview with Professor Marian Wesoły is available online with English subtitles on the website of the project Oral History and the Classics, here. We have already reported on shooting this interview here.

Professor Wesoły, at his desk at home, talked about his intellectual biography, his teachers, collaborators, colleagues, correspondents, about his academic adventures at research centres in Germany (Tübingen) and Italy (Naples), books and editions, and many other fascinating issues. Moreover, he shared his views on prospective developments of research in the field of ancient philosophy.
We want to encourage you, once again, to click here and watch the video.
The Ceremony of Presenting Doctoral Diplomas
In 2025 there were many important moments for the AΦR group, but one of the most remarkable of them took place on November the 20th. It was the ceremony of presenting the new doctors with their diplomas. The members of the AΦR group took part in such an event for the first time.
The degree holder was Mariam Sargsyan, (now Ph.D.!), who – after taking a traditional doctoral oath in Latin to the Rector Magnificus of the University of Zielona Góra, prof. dr hab. Wojciech Strzyżewski – was officially granted the doctoral title cum laude and the diploma by her academic supervisor, dr hab. Tomasz Mróz.
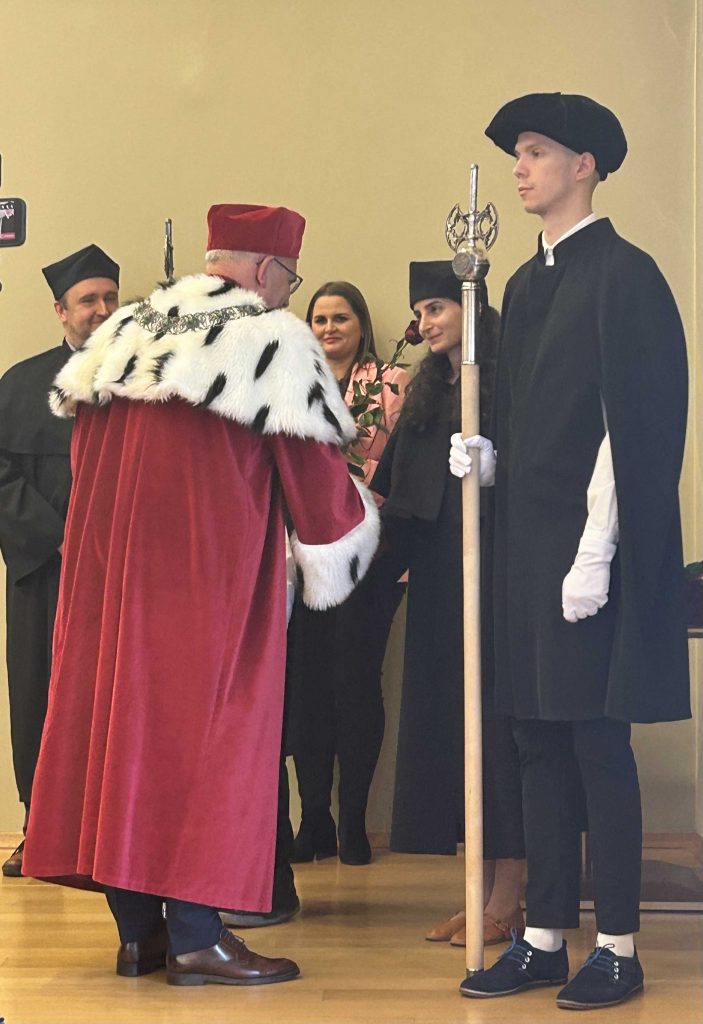

Some details of Sargsyan’s thesis and a report from her public defence can be found here, while all the information about the projects in which she participated, her activities and achievements can be found on our website tagged with M. Sargsyan or H. Jakubanis, whose life and works were the subject of her dissertation.
A full account of the ceremony on the university’s website, in Polish, can be found here.
Congratulations!
An Interview with our Vilnius Colleagues
As we announced this autumn, Research Council of Lithuania had decided to fund a research project on the reception of ancient philosophy in Vilnius University in the 20th century. Doc. dr Jonas Čiurlionis (Vilnius University) is the PI in this project, who leads the team consisting of dr Mindaugas Stoškus (VU) and dr hab. Tomasz Mróz (University of Zielona Góra).
This post is to advertise the interview with M. Stoškus and J. Čiurlionis, who talked about the project, its premises and objectives. The interview in written form has been recently published on the VU Faculty website in Lithuanian.

Both, J. Čiurlionis and M. Stoškus, focusing on Lithuanian period in the history of VU (1940-now), emphasised the need of philosophers to confront their outlooks, methods, and the very understanding of what philosophy is with ancient philosophers. They both spoke about their lecturers and how they had referred to the Greeks. We cannot agree more with them regarding their views on significance of Greek philosophy for each Western philosopher, philosophical current and national philosophical tradition. Thus it is important to research and assess the impact of Greek ideas on more recent philosophers, for the history of philosophy is not a linear development, but a constant reference to the roots of philosophical thinking. And the core aim of the project is to research who of the VU philosophers in the 20th century, why and how referred to and reflected on ancient philosophers.

Philosophy in Zielona Góra. An Anniversary
This year, Institute of Philosophy, University of Zielona Góra (UZ), where Ancient Φilosophy Reception research group is affiliated, celebrates its 30th anniversary. Among the variety of events, there was a conference on 23rd-24th October, devoted to the problem of co-operation in its various relations to theory, history and philosophical practice. AΦR’s history at UZ is obviously much shorter, but two of its representatives actively participated in the conference.

Mariam Sargsyan was the first of them. In her presentation she discussed the results of her doctoral studies at UZ and her dissertation, successfully defended earlier this year. She focused on analyses of Henryk Jakubanis’ (1879-1949) historical-philosophical legacy, which consists of three main parts: 1) his work on Empedocles and its methodology; 2) Plato in his (partly unpublished) writings; 3) his views on ancient and modern ways of doing philosophy. Moreover, Sargsyan presented the conclusions of her research on intellectual genealogy of Jakubanis’ thought.
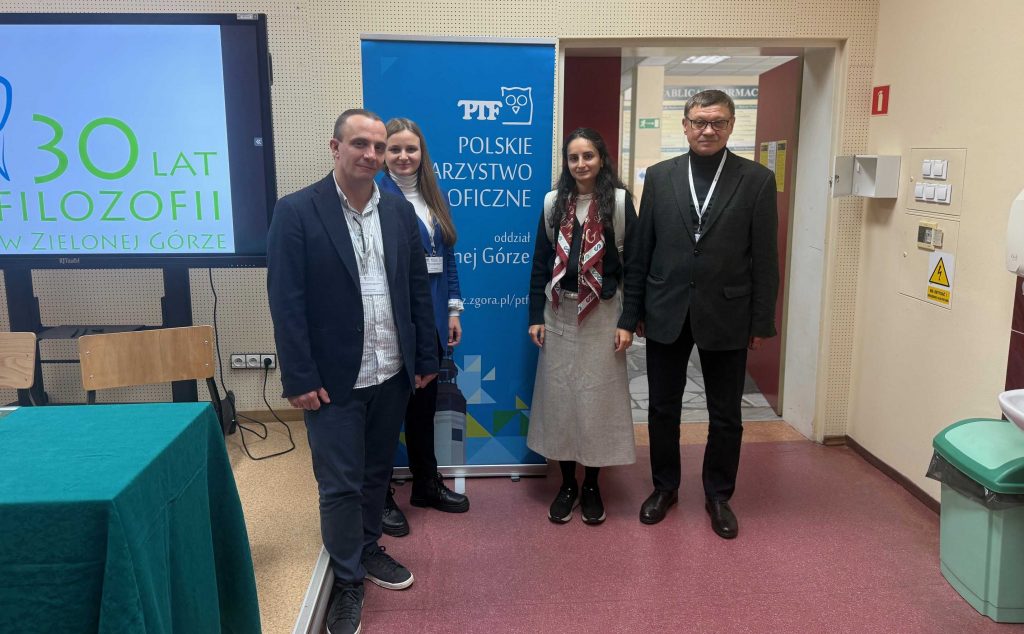

What was even more significant was the fact that Ukrainian participants (see the photo above) of the conference, who work at the National University of Kyiv, attended Sargsyan’s presentation on Jakubanis, who had studied and worked in Kyiv a century ago. They were very interested in her results and provided valuable feedback that could be helpful in improving the text of her doctoral thesis before it is published. The discussion between them demonstrated how important it is to confront different points of view on one subject which is researched by scholars from different countries, applying various methods and interested in different aspects of the history of philosophy.
The second conference participant from AΦR was Adrian Habura who delivered a paper on Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886-1980) and his reflection on social aspects of human happiness. Habura discussed Tatarkiewicz’s definition of happiness and his understanding of human life, then he examined the role of the others in individual happiness and the links between human individual and society in their relations to happiness. In his paper Habura developed a general view on the role of society in Tatarkiewicz’s philosophical and ethical considerations contained in his book Analysis of Happiness.
Although Habura’s paper was not directly devoted to the reception of ancient philosophy in Tatarkiewicz’s writings, the following discussion allowed him to address this issue. He highlighted some similarities and differences between Aristotle’s and Tatarkiewicz’s understandings of happiness and convincingly demonstrated how Aristotle could have inspired ethical investigations of this Polish philosopher, whose doctoral thesis on Aristotle was composed under supervision of the Marburg neo-Kantians.
A Centenary of the Kosciuszko Foundation
This year a merited institution supporting the development of Polish sciences, arts and humanities, Kosciuszko Foundation, celebrates its centennial anniversary. A decade ago Tomasz Mróz was a Kosciuszko Fellow at the University of Iowa, in the Department of Classics, whose Head at that time was Professor John Finamore.

On October 21st, 2025, in lecturing hall of the university’s library in Zielona Góra, T. Mróz delivered a talk about the history of the Kosciuszko Foundation and exchange programs for Polish scholars to pursue research visits in American academic institutions. The talk was based on the presentation provided by The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni, but its basic aim was to encourage prospective grantees to submit their project proposals and spend a couple of months in American universities. Moreover, Mróz shared his experience of preparing his proposal, of the interview and of many practical details of his 5 months research stay at the University of Iowa. The audience at the meeting was not numerous, yet highly motivated to develop their academic careers with support of the Foundation. A brief report from the meeting was published on the website of the University of Zielona Góra and on social media of the The Kosciuszko Foundation Alumni.


The talk induced Mróz to recall some memories of his stay in Iowa, in the Department of Classics. Financial support from the Foundation allowed him not only to cover flights, accomodation, and daily expenses, but also to undertake a research trip to the University of Chicago and the Joseph Regenstein Library, where essential manuscript collection for his research was preserved, that is, the legacy of Paul Shorey (1857-1934), an American Plato scholar…
…and Mróz’s project was focused, not surprisingly, on the reception of Plato, that is, on the controversy between Shorey and a Polish Plato scholar, Wincenty Lutosławski (1863-1954), over the methods of reading Plato’s dialogues, their chronological order, etc. During his stay Mróz delivered a paper on this topic at a seminar meeting in the Department of Classics.
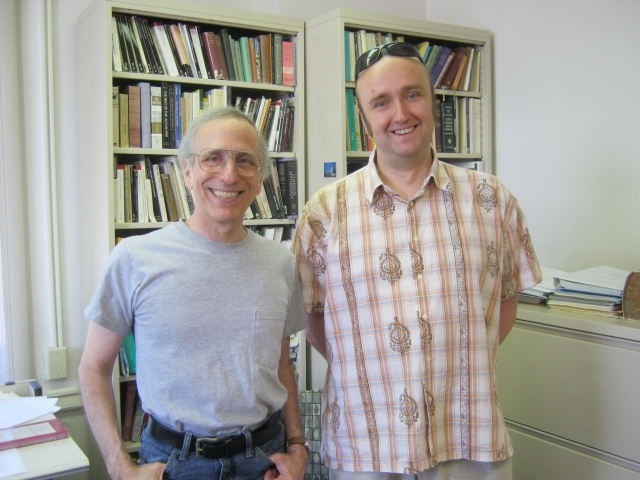


It all would not have been possible without a kind invitation from Professor John Finamore (on the left) who was at that time the Head of the Department of Classics and was very helpful for Mróz to settle in Iowa City, feel comfortable in the Department and do his research work in accordance to the plan. Thank you, John! It was a beneficial semester.
A Successful Project Proposal in Vilnius!
We are very glad to announce that the project proposal submitted by doc. dr Jonas Čiurlionis of Vilnius University to Research Council of Lithuania turned out to be successful! The title of the project in Lithuanian is Antikinės filosofijos recepcija XX a. Vilniaus universitete what translates into English as Reception of Ancient Philosophy in the 20th century Vilnius University.

Project will be pursued at the Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University (FsF VU), in 2025-2029. The scope of the project covers reception of ancient philosophy among scholars of Vilnius University, starting with the interwar, Polish period of its history, followed by the Soviet times after the World War II, concluding with research on ancient philosophy in free Republic of Lithuania.

The plan of the project includes organising a mid-term seminar meeting in Zielona Góra, an international conference in Vilnius, not to mention conference presentations and journal papers by all the three researchers employed in the project. And they are doc. dr Jonas Čiurlionis, Ph.D., head of the project and senior researcher, dr Mindaugas Stoškus, Ph.D., researcher, both of FsF VU, accompanied by dr hab. Tomasz Mróz, Ph.D., as senior researcher (UZ).
Recent commentaries