Home » Posts tagged 'Platonism' (Page 2)
Tag Archives: Platonism
AΦR at the 11th Seminar of the Historians of Polish Philosophy in Częstochowa
Seminar of the Historians of Polish Philosophy is a cyclic academic meeting which gathers philosophers and historians of philosophy who focus on the history of philosophy in Poland. 11th edition of this seminar was held in Częstochowa at Philosophy Department of Jan Długosz University on May 15th-16th, 2023, and it was focused, not surprisingly, on the topics of war and peace.

Two AΦR members delivered their papers there. Adrian Habura’s paper was not directly devoted to the reception of ancient philosophy, for he focused on the first edition of Władysław Tatarkiewicz’s (1886-1980) work O szczęściu [Analysis of Happiness] (1947), and took an attempt to analyse the content of the book and search for the topics related to war issues to determine possible origin of each chapter, that is, to divide the chapers into two groups: those composed by Tatarkiewicz before the outbreak of the World War II and those compose after it.
Tomasz Mróz, in turn, presented a largely unknown biography of a 20th century Polish researcher of Florentine neo-Platonism. His presentation had a long title: Bohdan Kieszkowski (1904-1997): a Researcher of Renaissance neo-Platonism and His Career Destroyed by the War (with the materials collected by Professor Czesław Głombik).
Kieszkowski published his works in Polish, Italian and French, and edited Conclusiones by Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (Geneve 1973). His opus vitae was the book Platonizm renesansowy [Renaissance Platonism] (Warszawa 1935), subsequently published in Italian as Studi sul platonismo del rinascimento in Italia (Firenze 1936). His studies were discussed mostly in Poland, Italy, France and Spain, but existing sources allowed only to reconstruct his biography to the first years after the World War II.
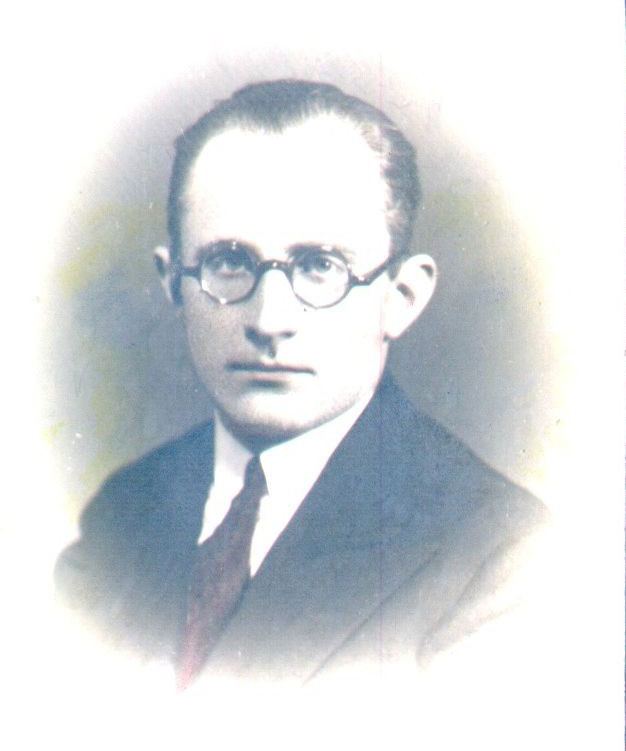


Materials collected by prof. C. Głombik (1935-2022) from family archives shed some light on Kieszkowski’s life on an exile in France. He was meeting there his former supervisor from the University of Warsaw, W. Tatarkiewicz, who was able to visit Paris several times in the sixties and considered Kieszkowski to be his best student. The letters from Tatarkiewicz to Kieszkowski’s sister, Wanda, reveal the facts concerning the details of a difficult life of a scholar on the exile. To Tatarkiewicz’s disappointed Kieszkowski was considering a turn in his focus from Renaissance studies to military history, yet he was very compassionate about his former student because he was aware of Kieszkowski’s physical and psychological limitations, resulting from his war and after war experiences. His legs, for example, were severely injured by German air raids already in 1939, he narrowly avoided amputation and throughout his life he experienced the negative effects of this until the end of his life. Communication between Tatarkiewicz and Kieszkowski was also affected by the fact that the former’s hearing was impaired and the latter spoke very quietly, as if he was afraid that someone could overhear them. Nevertheless, Kieszkowski’s works on Renaissance Platonism won recognition in the academic world and it is an interesting task to research their reception and impact.

A Monograph Book on Stanisław Lisiecki (and his Plato)

In a book series published by Marek Derewiecki a new volume has appeared. T. Mróz is the author and the title of the book is Stanisław Lisiecki (1872-1960) and His Plato (pp. 150). This book is a second one in the series and it complements volume one, which consisted mostly of unpublished materials produced by S. Lisiecki during his long and laborious life.
Apart from the foreword and concluding remarks, the book is divided into two main parts. The first part presents Lisiecki’s biography as fully as it has never been presented before. Numerous sources from the archival and manuscript collections from the libraries of Warsaw and Cracow were deployed to compose this chapter. Private, family materials were also used, including the photograph inside the book, an essential part of which was artistically remade to depict Lisiecki on the cover. His biography was divided into three chapters, which are separated from each other by two important facts in his life: leaving the clergy in 1921 and the outbreak of the World War II in 1939. The longest chapter is the middle one, between these two dates, because it was Lisiecki’s most productive period and it was possible to use numerous testimonies to document it.
Part two of the book discusses Lisiecki’s interpretation of Plato’s philosophy and its development. This part is divided into three parts as well. It presents Lisiecki’s views on the philosophical and spiritual evolution of Plato in three stages: Plato as a Socratic thinker, Plato in his mature works and Plato as an old sage. It was not possible to present Lisiecki’s views on all the important dialogues, for example on the Symposium or the Phaedrus, because his legacy is fragmentary and his comprehensive synthetic study on Plato had been destroyed during the war. Nevertheless, Plato in Lisiecki’s views is a half-religious thinker, an inspired poet and a visionary, whose creative personality was most fully expressed in his theory of the Good. The Good was sometimes identified by Lisiecki with God or with Providence and it transgressed dialectical formulation. Although Plato’s theory of reincarnation was assessed by Lisiecki as going too far, he found in it a consolation and an explanation of many phaenomena, for example, the inequality of talents among people.
Despite his admiration for Plato, Lisiecki did not avoid criticising him. Plato was for him a topical thinker and his dialogues – an intellectual challenge. We may say that Lisiecki, as many before him, was carried away by Plato’s enthusiasm, but he never lost sight of the deficiencies of Platonism.

This book is the final result of the research project on S. Lisiecki as a researcher of ancient Greek philosophy, sponsored by National Science Centre.
History of Philosophy in Poland in Martin-Luther-Universität Halle

Selected Topics in the History of Philosophy in Poland was the title of the course, which was delivered in May and June 2022 by Tomasz Mróz for the students of Martin-Luther-Universität (MLU) Halle in the building of the Steintor Campus (on the left). T. Mróz was appointed at MLU as Gastprofessor (funded by Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst DAAD) for a month at the Aleksander-Brückner-Zentrum für Polenstudien (Institut für Geschichte).
The course had a form of “Blockseminar” meetings and consisted of lectures, seminars and students’ presentations, focusing on various ideas, currents and problems in the history of philosophy in Poland. A course like this could not, obviously, do without a closer insight into some issues of ancient philosophy reception. For example, reception of Aristotle’s philosophy of nature in Vitello’s theory of demons and Pythagorean and Platonic inspirations in Copernicus were discussed. During one of the final lectures the problems of Plato reception in Poland were presented, as they were previosuly structured in the book Plato in Poland 1800-1950. The works of the following authors were briefly examined: A.I. Zabellewicz, F.A. Kozłowski, W. Tatarkiewicz, P. Semenenko, B. Limanowski, W. Dzieduszycki, E. Jarra, S. Pawlicki, W. Lutosławski, S. Lisiecki and W. Witwicki.


All the students attending the course in Polish philosophy should be thanked for their dilligence, co-operation and their presentations. The lectures, however, wouldn’t have taken place without the granting decision of professor Yvonne Kleinmann, who holds a chair in the East-European history at MLU and is the head of the Aleksander-Brückner-Zentrum für Polenstudien, and without co-ordinating work of doctor Paulina Gulińska-Jurgiel, to both of whom the lecturer is extremely grateful.
Recent commentaries