“Oral History and the Classics” Team in Katowice
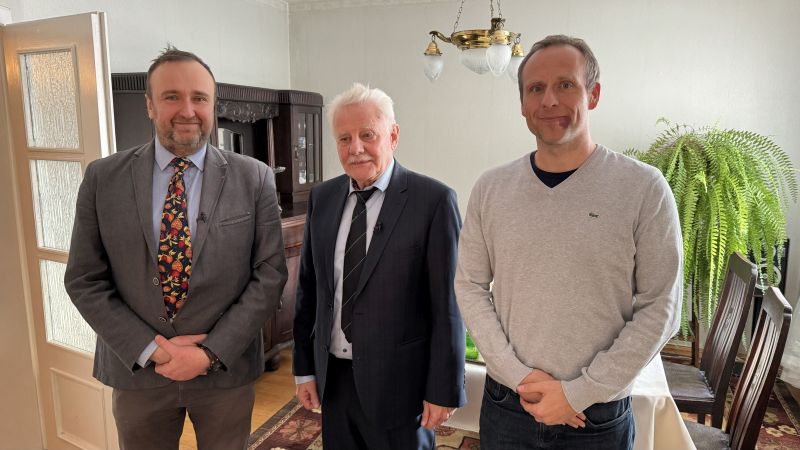
On Feb. 27th, 2023, Oral History and the Classics project team enjoyed the honour to visit Professor Bogdan Dembiński in the Library of The University of Silesia (Uniwersytet Śląski, UŚ) in Katowice. Profesor Dembiński is another Polish specialist in Greek philosophy who has agreed to give an interview which will be included in the Oral History and the Classics collection on the website of the University of Hradec Králové. In December 2023, as we have already announced, a similar interview was shot with prof. Andrzej Wesoły in Poznań.
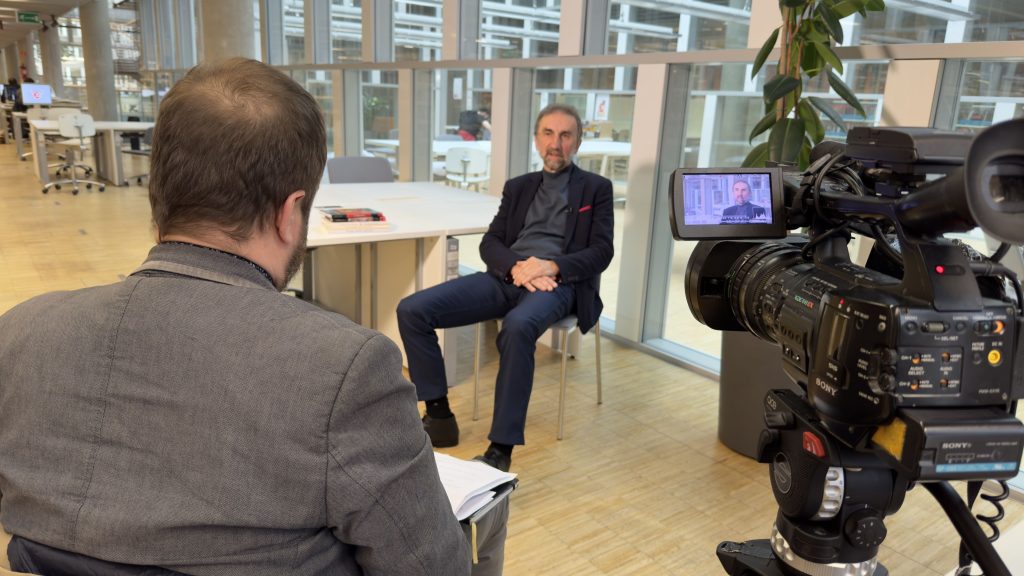

Bogdan Dembiński is currently a professor at UŚ, where he has taught and done his research work on Greek philosophy for almost four decades. Tomasz Mróz, who carried out the interview, in the last decade of the 20th century had been a participant in his lectures on ancient thought. The University of Silesia is not the only institution where prof. Dembiński delivers courses in philosophy. He teaches, for example, at The Karol Szymanowski Academy of Music in Katowice. He greatly appreciates this opportunity to introduce philosophy to the audiences who represent a different type of sensibility than philosophy students.
Having graduated in philosophy at the Catholic University of Lublin (KUL), Bogdan Dembiński returned to his home region of Silesia and received his Ph.D. on a thesis devoted to the philosophy of Martin Heidegger (1987). Apart from his university teachers it was Heidegger who induced him to focus on the everlasting legacy of Greek philosophy. Consequently, his postdoctoral thesis had Plato’s theory of ideas as its topic (1998) and subsequently Plato became the most important subject of his research. We shall add that prof. Dembiński was granted a title of the full professor in 2011 and then became a member of the Polish Academy of Arts and Sciences in Kraków.

The list of books on Plato, which were authored by Bogdan Dembiński, includes: Teoria idei – ewolucja myśli Platońskiej [Theory of Ideas – the evolution of Plato’s thought], 1997 and re-editions; Późna nauka Platona – związki ontologii i matematyki [The Late Philosophy of Plato – relations between ontology and mathematics], 2003; Późny Platon i Stara Akademia [The Late Plato and the Old Academy], 2010; Stara Akademia Platona [Plato’s Old Academy], 2018.
Prof. Dembiński spoke about his academic curriculum and emphasised his current involvement in scientific activities of the Copernicus Center for Interdiciplinary Studies, founded by prof. Michał Heller, the recipient of the Templeton Prize. In Dembiński’s view, ancient Greek reflection on the nature and cosmos should be continuously referred to, not only by philosophers, by also by the representatives of contemporary natural sciences, theoretical physics and cosmology, for profound Greek ideas still have the power to stimulate research in many fields.
When the whole recording is edited and furnished with English subtitles, it will be make public and available on the project’s website. The interview meeting with prof. Dembiński would not be possible without his kind consent and hospitality of the UŚ Library staff. The interview was carried out by T. Mróz, while Jan Kadeřábek, a cinematographer and a cameraman, took care of all the technicalities.

A Review of Plato in Poland 1800-1950
It is our honour to announce that the second review of the book Plato in Poland 1800-1950. Types of Reception – Authors – Problems (Academia, Baden Baden 2021) has just seen the light of day (the first one was announced here). The review was published in “Revue Philosophique de Louvain” 2023 (vol. 120, 1).

The review was kindly composed by professor Sylvain Delcomminette (Université Libre de Bruxelles). Professor Delcomminette is an expert in Plato’s philosophy, his current research topics include the reception of Platonism in the Marburg neo-Kantian school and specific issues in the philosophy of Aristotle. For us, one of the most important conclusions in prof. Delcomminette’s review is that the reader of this book will not get bored. Thus our task is done.
Full text of the review can be downloaded from the journal’s website
(with a personal account) here.
Vilnius and Ancient Philosophy
Institute of Philosophy, University of Zielona Góra (UZ), has for many years developed co-operation with Vilnius University (VU) in the framework of Erasmus+ programme. UZ philosophers, members of the faculty or students, visit Vilnius, and VU philosophers visit Zielona Góra almost every academic year, as we have recently reported here and here.
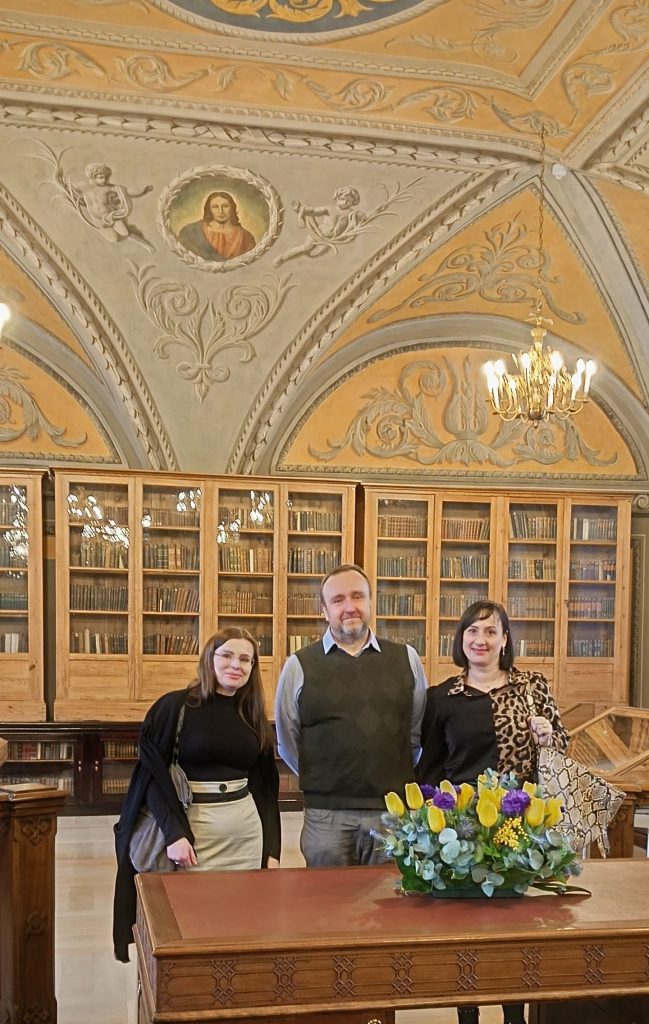

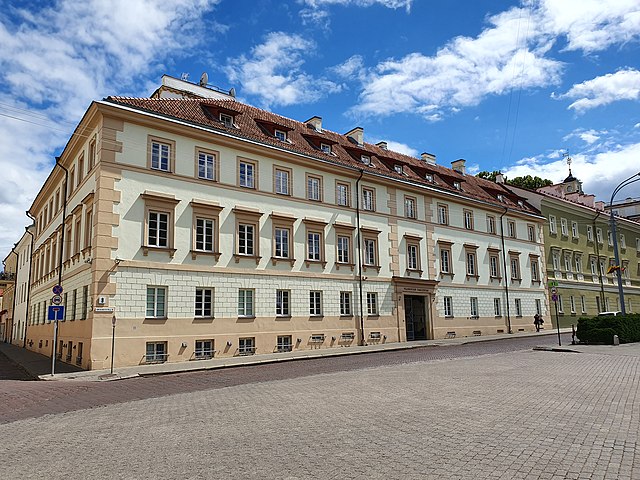
On Feb. 6-7th representatives of AΦR (Tomasz Mróz) and academic staff of the Institute (Justyna Kroczak, Joanna Zegzuła-Nowak) paid a working visit to Vilnius philosophers to discuss possibilities of expanding future research co-operation on the topics related to the reception of ancient philosophy.
Visiting group was given a tour of the old library of VU. The visit was an opportunity for UZ scholars to investigate possibilitites of a library query in special collections of VU and to learn the library regulations and new restrictions for readers who research manuscripts and old prints.
On the photo: J. Kroczak, T. Mróz, J. Zegzuła-Nowak in the historic Franciszek Smuglewicz Hall, VU, the old library.
The trip to Vilnius was funded from the “Small Grant” allocated last year to T. Mróz by the Deputy Rector of the University of Zielona Góra.
A paper on Polish translations of Plato
The latest issue of the “Revue de philosophie ancienne” (2023/2, vol. XLI) includes a paper by T. Mróz: Polish Translations of Plato’s Dialogues from the Beginnings to the Mid-Twentieth Century.

In his paper T. Mróz focuses on four most significant translators of Plato’s dialogues in Poland. They were: Felicjan Antoni Kozłowski (1805-1870), who was the first translator of Plato into Polish; Antoni Bronikowski (1817-1884), who was the most productive in the 19th century and kept on working on Plato in spite of unfavourable reviews; Stanisław Lisiecki (1872-1960), whose numerous translations remained unpublished; and finally Władysław Witwicki (1878-1948), whose renderings of the dialogues are still widely read. The paper presents their achievements and discusses the reception of their works.
Anyone whishing to receive an offprint should feel free to request it from the author via email.
“Oral History and the Classics” Team in Poznań
On Dec. 5th, 2023, Oral History and the Classics project team enjoyed the honour to visit Professor Marian Andrzej Wesoły at his home, in the vicinity of Poznań. Prof. Wesoły agreed to give an interview which will be included in the Oral History and the Classics collection on the website of the University of Hradec Králové.
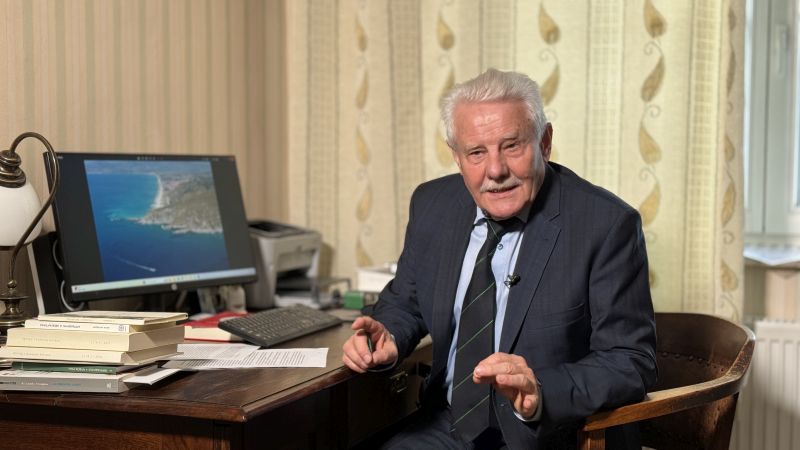

Marian Wesoły is currently a professor emeritus of Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań and lectures at the Jacob of Paradies Academia in Gorzów Wielkopolski. His entire academic career in Poland was connected to Poznań and Adam Mickiewicz University. His doctoral (1977) and postdoctoral (1992) dissertations were devoted to the history of Greek philosophy. In 2008 he received the title of a full professor. He was granted several foreign scholarships, e.g. in Italy (1980: University of Padova, 1983: Italian Institute for History in Naples, 1997: Villa I Tatti), Germany (1986/87: University of Tübingen), and Greece (1993, 2000, 2012: Academy of Athens). Prof. Wesoły is a co-founder of the „Peitho. Examina Antiqua” journal. For 20 years he has regularly participated in the Eleatica-Symposia, initiated by Prof. Livio Rossetti at the Alario Foundation in Ascea, close to the ruins of ancient Elea/Velia. Finally, we should mention that on the 100th anniversary of the Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań (2019) he was awarded Knight’s Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta.

Prof. Wesoły is a specialist in Greco-Roman and Byzantine philosophies. In his numerous works he attempts to combine philological analyses with philosophical interpretation. Moreover, he is active as a translator and one of his most recent productions is a bilingual edition and commentary of Aristotle’s Analytica Priora et Posteriora (2020).
During the interview prof. Wesoły reflected on his academic and research curriculum, but also shared his views on perspectives of his discipline, on political constraints in researching ancient philosophy, recalled his memories of the great scholars whom had the opportunity to meet and with whom he collaborated etc. When the whole recording is edited and furnished with English subtitles, it will be make public and available on the project’s website.
The interview meeting with prof. Wesoły would not be possible without his kind consent and warm welcome of the team members by his family at their home. Those were Tomasz Mróz and Jaroslav Daneš who carried out the interview, while Jan Kadeřábek, a cinematographer and a cameraman, took care of all the technicalities.

“Small Grant” from the University of Zielona Góra

Prof. Marcin Mrugalski, the Deputy Rector of the University of Zielona Góra (UZ), home institution of the AΦR, awarded Tomasz Mróz with a “Small Grant” of a maximum possible value. These internal grants are distributed by the Rector annually among those researchers of UZ, who had submitted their proposals to the National Science Centre (NCN), received positive assessements from the experts, yet finally had not been granted funding. Aim of the “Small Grants” is to increase the chances of the researches in future granting competitions.
“Small Grant” funds for AΦR will be spent on developing and strenghtening a co-operation between AΦR members and the Institute of Philosophy (UZ) with colleagues from the Faculty of Philosophy, Vilnius University (VU), on the topic of the history of research on ancient philosophy in VU during its complex history.

AΦR at the Twelfth Polish Congress of Philosophy in Łódź
In September (11th-16th) 2023 the 12th Polish Congress of Philosophy took place in Łódź. Three members of AΦR took part in this great event, and they delivered four papers there. Tomasz Mróz spoke about three traditions of doing philosophy and three interpretations of Plato at the ancient philosophy section, and the other three papers were presented in the section of Polish philosophy: on the influence of Aristotle on the works of W. Tatarkiewicz (Adrian Habura); on H. Jakubanis’ arguments for the reneval of philosophy in accordance to its ancient roots (Mariam Sargsyan); and on B. Kieszkowski, a researcher of Renaissance Platonism, on his life, works and their reception (again T. Mróz).

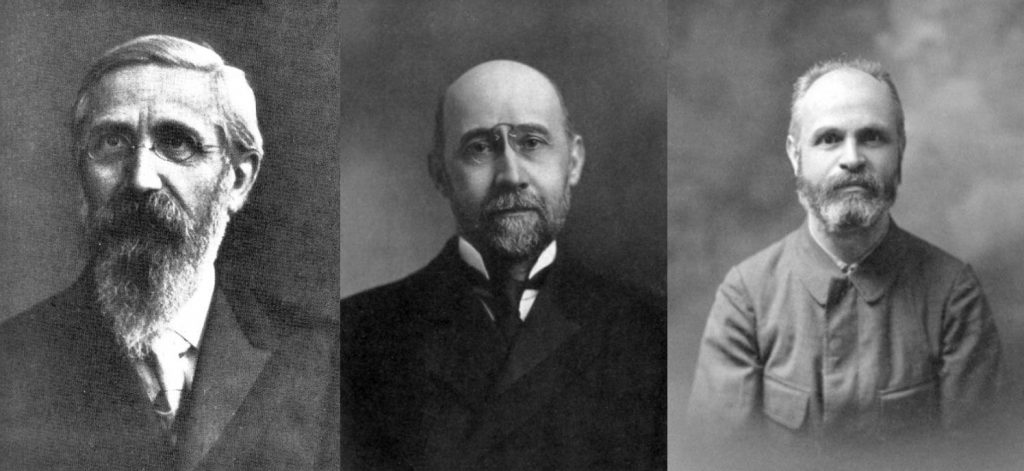
T. Mróz’s paper, Three Traditions of Doing Philosophy and Three Interpretations of Plato, was devoted to presenting three Plato scholars of the turn of the 20th century, Paul Natorp (1854–1924), a German, Paul Shorey (1857–1934), an American, and Wincenty Lutosławski (1863–1954), a Pole, and their interpretations of Plato. Mróz attempted to relate these three personalities of one generation and their Platonic studies with their native, dominant philosophical traditions: neo-Kantianism, Emersonian tradition and Polish Romantic Messianism. Their methodologies, views on the chronology of the dialogues and the status of ideas were discussed, as a starting point for future comparative research of their Platonic studies and reciprocal references.

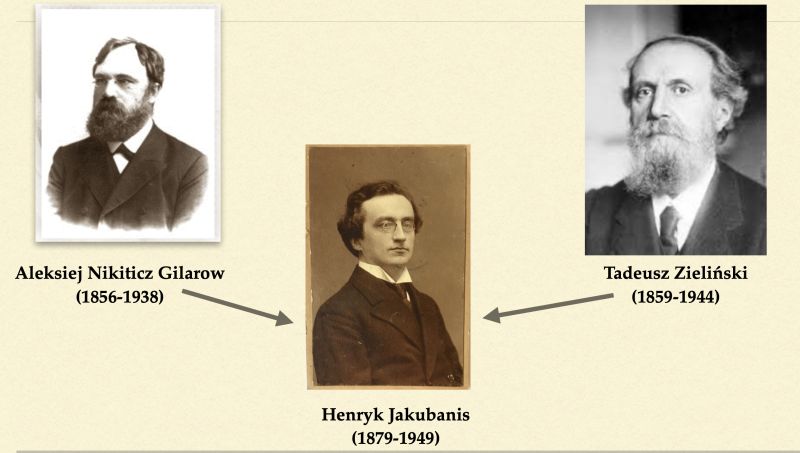
M. Sargsyan’s presentation was titled: Arguments of Henryk Jakubanis (1879-1949) for Renewal of Philosophy and Culture on the Ancient Model. It started with an introductory part about the biography of Jakubanis to familiarise the audience with his personality. Then the main part followed and it consisted in discussing Jakubanis’ work The Significance of Ancient Philosophy for the Modern View of the World (1910). Historical and philosophical research methods of Jakubanis were analysed and compared with those of his academic supervisor in Kyiv, Alexei Gilarov. Another comparative perspective was provided by the works of Tadeusz Zielinski, who was an internationally recognised scholar, and a kind, older colleague for Jakubanis.
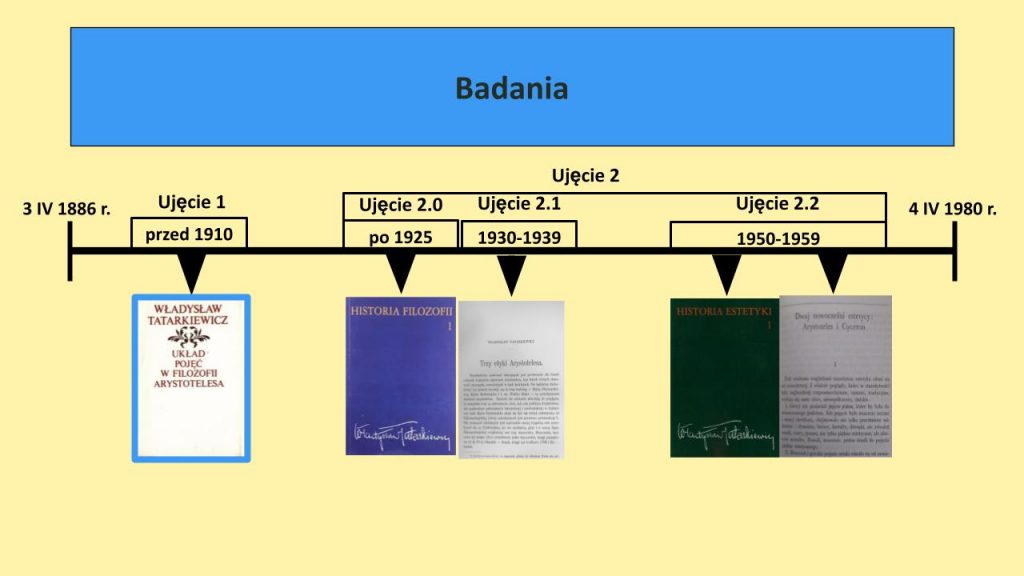
A. Habura’s paper was titled Aristotle in the Works of Władysław Tatarkiewicz and divided into two parts. In the first one, following Tatarkiewicz’s own statement, Habura distinguished two “images” of Aristotle’s philosophy which Tatarkiewicz had developed during his research career. Habura took into account various works of Tatarkiewicz and demonstrated that these two images were not contradictory, but rather complementary to each other. In the second part of his presentation Habura distinguished five aspects of Aristotle’s inspiration in Tatarkiewicz’s works, in accordance with Tatarkiewicz’s own reflection on this topic, and proved a significant, substantial and lasting impact of Aristotle on Tatarkiewicz’s original philosophical investigations.
Second paper by Mróz was a presentation of a further development of his research on Bohdan Kieszkowski, a Polish scholar who was a specialist on Renaissance Platonism and Pico della Mirandola. Earlier this year Mróz discussed Kieszkowski’s biography, but this time the focus was on Kieszkowski’s works and their reception, that is, his polemic with another Polish expert in Renaissance philosophy, M. Heitzman (1899-1964), on the sources of Renaissance Italian Platonism, and a critical reception of Kieszkowski’s edition of Pico’s Conclusiones (1973) by a Portuguese researcher, José Vitorino de Pina Martins (1920-2010). Heitzman searched for the roots of philosophy in Florentine Academy in medieval thought, while Kieszkowski tended to emphasise the role of ancient sources. As for Pina Martins, he praised Kieszkowski’s erudition, yet pointed to a large number of errors in Conclusiones, resulting from various reasons, including Kieszkowski’s lack of precision in reading Latin texts.

Recent commentaries